Prevalence, Impact, and Diagnostic Challenges of Benign Breast Disease: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 37223067
- PMCID: PMC10202205
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S351095
Prevalence, Impact, and Diagnostic Challenges of Benign Breast Disease: A Narrative Review
Abstract
Benign breast diseases, which are commonly seen in clinical practice, have various clinical presentations and implications, as well as management strategies. This article describes common benign breast lesions, presentations of these lesions, and typical radiographic and histologic findings. Also included in this review are the most recent data and guideline-based recommendations for the management of benign breast diseases at diagnosis, including surgical referral, medical management, and ongoing surveillance.
Keywords: breast biopsy; imaging; management; surveillance.
© 2023 Fraker et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
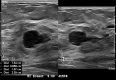
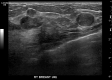
Figures

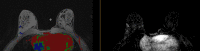


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

