A Pilot Study on Blood Components in COVID-19 Affected Subjects: A Correlation to UPR Signalling and ER-Stress
- PMID: 37223306
- PMCID: PMC9997434
- DOI: 10.1007/s12291-023-01121-8
A Pilot Study on Blood Components in COVID-19 Affected Subjects: A Correlation to UPR Signalling and ER-Stress
Abstract
Abstract: The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the site for protein synthesis, its folding and secretion. An intricate set of signalling pathways, called UPR pathways, have been evolved by ER in mammalian cells, to allow the cell to respond the presence of misfolded proteins within the ER. Breaching of these signalling systems by disease oriented accumulation of unfolded proteins may develop cellular stress. The aim of this study is to explore whether COVID-19 infection is responsible for developing this kind of endoplasmic reticulum related stress (ER-stress). ER-stress was evaluated by checking the expression of ER-stress markers e.g. PERK (adapting) and TRAF2 (alarming). ER-stress was correlated to several blood parameters viz. IgG, pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, leukocytes, lymphocytes, RBC, haemoglobin and PaO2/FiO2 ratio (ratio of arterial oxygen partial pressure to fractional inspired oxygen) in COVID-19 affected subjects. COVID-19 infection was found to be a state of protein homeostasis (proteostasis) collapse. Changes in IgG levels showed very poor immune response by the infected subjects. At the initial phase of the disease, pro-inflammatory cytokine levels were high and anti-inflammatory cytokines levels were low; though they were partly compromised at later phase of the disease. Total leukocyte concentration increased over the period of time; while percentage of lymphocytes were dropped. No significant changes were observed in cases of RBC counts and haemoglobin (Hb) levels. Both RBC and Hb were maintained at their normal range. In mildly stressed group, PaO2/FiO2 ratio (oxygenation status) was in the higher side of normal range; whereas in other two groups the ratio was in respiratory distress syndrome mode. Virus could induce mild to severe ER-stress, which could be the cause of cellular death and systemic dysfunction introducing fatal consequences.
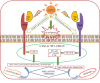
Graphical abstract: Schematic representation of SARS-CoV-2 infection and related consequences.
Keywords: COVID-19; ER-stress; IgG response; PERK; Protein misfolding; TRAF2; Unfolded protein response.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Association of Clinical Biochemists of India 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A journey in UPR modelling.Biol Cell. 2023 Apr;115(4):e2200111. doi: 10.1111/boc.202200111. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Biol Cell. 2023. PMID: 36751133 Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum proteostasis: a key checkpoint in cancer.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017 Feb 1;312(2):C93-C102. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00266.2016. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27856431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and unfolded protein response in inflammatory bowel disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015 Mar;21(3):636-44. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000238. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015. PMID: 25581827
-
Imaging of single cell responses to ER stress indicates that the relative dynamics of IRE1/XBP1 and PERK/ATF4 signalling rather than a switch between signalling branches determine cell survival.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Sep;22(9):1502-16. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.241. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 25633195 Free PMC article.
-
Misfolded proteins bind and activate death receptor 5 to trigger apoptosis during unresolved endoplasmic reticulum stress.Elife. 2020 Jan 6;9:e52291. doi: 10.7554/eLife.52291. Elife. 2020. PMID: 31904339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salari N, Hosseinian-Far A, Jalali R, Vaisi-Raygani A, Rasoulpoor S, Mohammadi M, Rasoulpoor S, Khaledi-Paveh B, et al. Prevalence of stress, anxiety, depression among the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Glob Health. 2020;16:57. doi: 10.1186/s12992-020-00589-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
