Sterol carrier protein 2: A promising target in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 37223526
- PMCID: PMC10201558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2021.12.007
Sterol carrier protein 2: A promising target in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis
Abstract
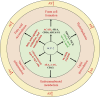
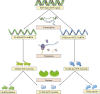
Atherosclerosis, the underlying pathophysiological basis of cardiovascular disease, has been recognized as a lipid-driven chronic inflammatory disease. Sterol carrier protein 2 (SCP-2) is a 13-kDa non-specific lipid-transfer protein expressed by various tissues and cells, such as liver, heart, vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), and macrophages. SCP-2 has an extensive role in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Recently, SCP-2 was reported to promote the development of atherosclerosis by regulating lipid metabolism and peroxidation, endocannabinoid metabolism, vascular inflammation, and fatty acid metabolism. In this review, we summarized the recent advances regarding the role of SCP-2 in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and tried to provide a rationale for future investigation and a better understanding of the biological functions of SCP-2 in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Fatty acid metabolism; Lipid metabolism; SCP-2; Vascular inflammation.
© 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Scannapieco F.A., Bush R.B., Paju S. Associations between periodontal disease and risk for atherosclerosis, cardiovascular disease, and stroke. A systematic review. Ann Periodontol. 2003;8(1):38–53. - PubMed
-
- Anand S.S., Yusuf S., Vuksan V., et al. Differences in risk factors, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease between ethnic groups in Canada: the Study of Health Assessment and Risk in Ethnic groups (SHARE) Lancet. 2000;356(9226):279–284. - PubMed
-
- Maguire E.M., Pearce S.W.A., Xiao Q. Foam cell formation: a new target for fighting atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Vasc Pharmacol. 2019;112:54–71. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

