Oncolytic viruses: A novel treatment strategy for breast cancer
- PMID: 37223527
- PMCID: PMC10201557
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2021.11.011
Oncolytic viruses: A novel treatment strategy for breast cancer
Abstract
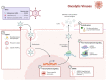
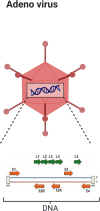
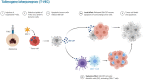
Breast cancer, an unceasingly occurring neoplasm, is one of the major determinants of mortality in women. Several ineffective attempts have been pursued using with conventional therapies against breast cancer. Resistance to existing therapies and their respective debilitating adverse effects have led research toward a new era of cancer treatment using viruses. Virotherapy constitutes a developing treatment modality with multiple mechanisms of therapeutic activity in which the viruses can be directly oncolyticand can express transgenes or induce host immune response against tumor cells. Several different DNA- and RNA-containing viruses have been considered for virotherapy of breast cancer including adenovirus, herpes virus, vaccinia, reovirus, Newcastle Disease virus, measles virus and vesicular stomatitis virus. This review aims to summarize the viro-therapeutical agents against breast malignancies. Key Scientific Concepts of Review: In this review paper, we proposed a new strategy to virus's combinatorial treatments using several kinds of transgenes and drugs. These recombinant viruses have provided evidence of treatment efficacy against human breast cancer.
Keywords: Adenovirus; Breast cancer; Herpes virus; Measles virus; Newcastle disease virus; Reovirus; Vaccinia; Vesicular stomatitis virus; Virotherapy.
© 2021 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sahin T.T., Kasuya H., Nomura N., et al. Impact of novel oncolytic virus HF10 on cellular components of the tumor microenviroment in patients with recurrent breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2012;19(4):229–237. - PubMed
-
- Ranki T., Särkioja M., Hakkarainen T., et al. Systemic efficacy of oncolytic adenoviruses in imagable orthotopic models of hormone refractory metastatic breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2007;121(1):165–174. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

