A novel coumarin derivative DBH2 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells
- PMID: 37223541
- PMCID: PMC10201669
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.08.021
A novel coumarin derivative DBH2 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of chronic myeloid leukemia cells
Abstract
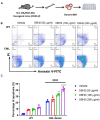
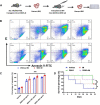
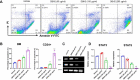
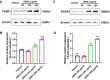
With the development of tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) resistance, finding the novel effective chemotherapeutic agent is of seminal importance for chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) treatment. This study aims to find the effective anti-leukemic candidates and investigate the possible underlying mechanism. We synthesized the novel coumarin derivatives and evaluated their anti-leukemic activity. Cell viability assay revealed that compound DBH2 exhibited the potent inhibitory activity on the proliferation of CML K562 cells and TKI resistant K562 cells. Morphological observation and flow cytometry confirmed that DBH2 could selectively induce cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase of the K562 cells, which was further confirmed on the bone marrow cells from CML transgenic model mice and CD34+ bone marrow leukemic cells from CML patients. Treatments of DBH2 in combination with imatinib could prolong the survival rate of SCL-tTA-BCR/ABL transgenic model mice significantly. Quantitative RT-PCR revealed that DBH2 inhibited the expression of STAT3 and STAT5 in K562 cells, and caspase-3 knockout alleviated the DBH2 induced apoptosis. Furthermore, DBH2 could induce the expression of PARP1 and ROCK1 in K562 cells, which may play the important role in caspase-dependent apoptosis. Our results concluded that coumarin derivative DBH2 serves as a promising candidate for the CML treatment, especially in the combination with imatinib for the TKI resistant CML, and STAT/caspase-3 pathway was involved in the molecular mechanism of anti-leukemic activity of DBH2.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Caspase; Chronic myeloid leukemia; Coumarin; STAT.
© 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Apperley J.F. Chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet. 2015;385(9976):1447–1459. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

