Human Platelet-Rich Plasma Regulates Canine Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration through Aquaporins
- PMID: 37223543
- PMCID: PMC10202607
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/8344259
Human Platelet-Rich Plasma Regulates Canine Mesenchymal Stem Cell Migration through Aquaporins
Abstract
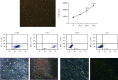
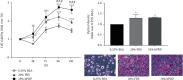
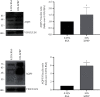
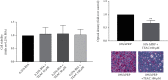
Platelet products are commonly used in regenerative medicine due to their effects on the acceleration and promotion of wound healing, reduction of bleeding, synthesis of new connective tissue, and revascularization. Furthermore, a novel approach for the treatment of damaged tissues, following trauma or other pathological damages, is represented by the use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). In dogs, both platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and MSCs have been suggested to be promising options for subacute skin wounds. However, the collection of canine PRP is not always feasible. In this study, we investigated the effect of human PRP (hPRP) on canine MSCs (cMSCs). We isolated cMSCs and observed that hPRP did not modify the expression levels of the primary class of major histocompatibility complex genes. However, hPRP was able to increase cMSC viability and migration by at least 1.5-fold. hPRP treatment enhanced both Aquaporin (AQP) 1 and AQP5 protein levels, and their inhibition by tetraethylammonium chloride led to a reduction of PRP-induced migration of cMSCs. In conclusion, we have provided evidence that hPRP supports cMSC survival and may promote cell migration, at least through AQP activation. Thus, hPRP may be useful in canine tissue regeneration and repair, placing as a promising tool for veterinary therapeutic approaches.
Copyright © 2023 Alessia Parascandolo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hyperbaric oxygen potentiates platelet-rich plasma composition and accelerates bone healing.J Orthop Translat. 2025 Jan 19;51:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.10.016. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 39902098 Free PMC article.
-
Promising cell-based therapy for bone regeneration using stem cells from deciduous teeth, dental pulp, and bone marrow.Cell Transplant. 2011;20(7):1003-13. doi: 10.3727/096368910X539128. Epub 2010 Nov 5. Cell Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21054950
-
[Effects of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and platelet-rich plasma on healing of wounds with full-thickness skin defects in mice].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018 Dec 20;34(12):887-894. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2018.12.013. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30585053 Chinese.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Canine Medicine.Arch Razi Inst. 2021 Oct 31;76(4):721-730. doi: 10.22092/ari.2021.355953.1749. eCollection 2021 Oct. Arch Razi Inst. 2021. PMID: 35096308 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage regeneration in dogs.World J Stem Cells. 2019 May 26;11(5):254-269. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i5.254. World J Stem Cells. 2019. PMID: 31171954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Platelet-Derived Growth Factor as Biomarker of Clinical Outcome for Autologous Platelet Concentrate Therapy in Grade I Knee Osteoarthritis.Biologics. 2025 Mar 25;19:137-147. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S500522. eCollection 2025. Biologics. 2025. PMID: 40161859 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet Concentrates Preconditioning of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Combined Therapies: Integrating Regenerative Strategies for Enhanced Clinical Applications.Cell Transplant. 2024 Jan-Dec;33:9636897241235460. doi: 10.1177/09636897241235460. Cell Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38506426 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

