PET/MRI Applications in Pediatric Epilepsy
- PMID: 37223623
- PMCID: PMC10202574
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-1764303
PET/MRI Applications in Pediatric Epilepsy
Abstract
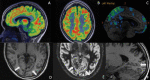
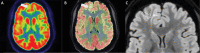
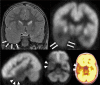
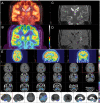
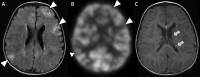
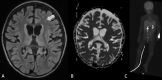
Epilepsy neuroimaging assessment requires exceptional anatomic detail, physiologic and metabolic information. Magnetic resonance (MR) protocols are often time-consuming necessitating sedation and positron emission tomography (PET)/computed tomography (CT) comes with a significant radiation dose. Hybrid PET/MRI protocols allow for exquisite assessment of brain anatomy and structural abnormalities, in addition to metabolic information in a single, convenient imaging session, which limits radiation dose, sedation time, and sedation events. Brain PET/MRI has proven especially useful for accurate localization of epileptogenic zones in pediatric seizure cases, providing critical additional information and guiding surgical decision making in medically refractory cases. Accurate localization of seizure focus is necessary to limit the extent of the surgical resection, preserve healthy brain tissue, and achieve seizure control. This review provides a systematic overview with illustrative examples demonstrating the applications and diagnostic utility of PET/MRI in pediatric epilepsy.
Keywords: PET/MRI; focal cortical dysplasia; hybrid imaging; malformations of cortical development; mesial temporal sclerosis; pediatric epilepsy; temporal lobe epilepsy; tuberous sclerosis.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest Heike Daldrup-Link reported below details: Grants or contracts from any entity: R01AR054458 (PI), R01HD081123 (PI), R21AR075863 (PI), R21HD103638 (PI), U24CA264298 (Co-PI), P30CA124435 (Key personnel) Andrew McDonough B+ Foundation ReMission Alliance Sarcoma Foundation of America. Royalties or licenses: US20130344003, WO2015014756, WO2018217943 Monasteria Press LLC Patents: US20130344003, WO2015014756, WO2018217943. Participation on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board: External advisory board member, R24OD019813-01 Advisory board member, Stanford Cancer Imaging T32 Training Program, 5 T T32 Act CA009695 Project 29 Advisory Board, The Lancet Hematology Leadership or fiduciary role in other board, society, committee or advocacy group, paid or unpaid: Member, Editorial Board, Nanotheranostics Member, Editorial Board, Journal of Nuclear Medicine Associate Editor, Radiology: Imaging Cancer Co-Program Director, Mentoring to AdVance womEN in Science (MAVENS) program, Stanford School of Medicine, Associate Chair for Diversity, Department of Radiology, Stanford School of Medicine Co-Director, Cancer Imaging & Early Detection Program, Stanford Cancer Institute, 5P30CA124435-10 Board Member, SPR Research Foundation, Society for Pediatric Radiology (SPR) Member, Noninterpretive Skills and Practice Management Committee, Annual Meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) Awards Committee, World Molecular Imaging Society (WMIS) Ana Franceschi reported: Grants or contracts from any entity: Foundation of the ASNR Boerger Grant. Consulting fees: Biogen, Life Molecular Imaging, Genentech. Leadership or fiduciary role in other board: Chair, ACR Neuroradiology Commission Dementia Workgroup. All other authors reported no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

