Renoprotective Effect of Thai Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with SGLT-2 Inhibitors versus DPP-4 Inhibitors: A Real-World Observational Study
- PMID: 37223658
- PMCID: PMC10202602
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/5581417
Renoprotective Effect of Thai Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with SGLT-2 Inhibitors versus DPP-4 Inhibitors: A Real-World Observational Study
Abstract
Background: Recently, there is a lack of studies comparing the renoprotective effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. This study therefore aimed to investigate the renoprotective effects of SGLT-2 inhibitors and DPP-4 inhibitors on Thai patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods: Patient medication records of all patients who used those two antidiabetic classes at Fort Wachirawut Hospital were reviewed. Renal function tests, blood glucose levels, and other baseline characteristics were collected. Continuous variables were compared within the group using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and between groups using the Mann-Whitney U test.
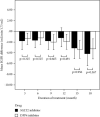
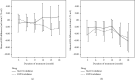
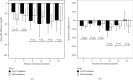
Results: There were 388 and 691 patients with SGLT-2 inhibitors and DPP-4 inhibitors, respectively. The mean estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of the SGLT-2 inhibitor group was significantly lower from baseline at 18 months of treatment, as well as the DPP-4 inhibitor group. However, the trend of eGFR reduction in patients with baseline eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 was smaller than those with baseline eGFR ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2. In addition, the fasting blood sugar and haemoglobin A1c levels significantly decreased from baseline in both the groups.
Conclusions: Both SGLT-2 inhibitors and DPP-4 inhibitors showed the same trends of eGFR reductions from baseline in Thai patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. However, SGLT-2 inhibitors should be considered in patients with impaired renal function rather than in all T2DM patients.
Copyright © 2023 Apichaya Chanawong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renoprotective effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors among type 2 diabetes patients with different baseline kidney function: a multi-center study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Oct 7;20(1):203. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01396-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 34620182 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective analysis of the effect of SGLT-2 inhibitors on renal function in patients with type 2 diabetes in the real world.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 5;15:1376850. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1376850. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39161902 Free PMC article.
-
Should Baseline Hemoglobin A1c or Dose of SGLT-2i Guide Treatment With SGLT-2i Versus DPP-4i in People With Type 2 Diabetes? A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.J Clin Pharmacol. 2020 Aug;60(8):980-991. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1599. Epub 2020 May 12. J Clin Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32396236
-
Metabolic effectiveness of gliflozins and gliptins in the routine clinical practice of patients with type 2 diabetes: preliminary results from GIOIA, a prospective multicentre study.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019 Sep;155:107787. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107787. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019. PMID: 31326454
-
An update on the safety and efficacy of oral antidiabetic drugs: DPP-4 inhibitors and SGLT-2 inhibitors.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2019 Aug;18(8):691-701. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2019.1626823. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2019. PMID: 31150300 Review.
References
-
- Saeedi P., Petersohn I., Salpea P., et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice . 2019;157 doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843.107843 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
