Italian version of the Brief Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders (Brief-IT-QOD)
- PMID: 37224170
- PMCID: PMC10366567
- DOI: 10.14639/0392-100X-N2212
Italian version of the Brief Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders (Brief-IT-QOD)
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the reliability and validity of the Italian version of the Brief Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders (Brief-IT-QOD).
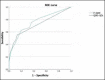
Methods: The study consisted of six phases: item generation, reliability analysis (112 dysosmic patients for internal consistency analysis and 61 for test-retest reliability analysis), normative data generation (303 normosmic subjects), validity analysis (comparison of Brief-IT-QOD scores of healthy and dysosmic subjects and scores correlation with psychophysical olfactory testing TDI and SNOT-22 scores), responsiveness analysis (10 dysosmic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps patients before and after biologic therapy), and cut-off value determination (ROC curve analysis of Brief-IT-QOD sensitivity and specificity).
Results: All subjects completed the Brief-IT-QOD. Internal consistency (α > 0.70) and test-retest reliability (ICC > 0.7) were acceptable and satisfactory for both questionnaire subscales. A significant difference between dysosmic and control subjects was found in both subscales (p < 0.05). Significant correlations between subscales scores and TDI and SNOT-22 scores were observed. Brief-IT-QOD scores before treatment were significantly higher than after biological therapy.
Conclusions: Brief-IT-QOD is reliable, valid, responsive to changes in QoL, and recommended for clinical practice and outcome research.
Versione italiana del brief Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders (Brief-IT-QOD).
Obiettivo: Valutare affidabilità e validità della versione italiana del Questionario Breve dei Disordini Olfattivi (Brief-IT-QOD).
Metodi: Lo studio è stato composto da sei fasi: generazione del questionario, analisi di affidabilità (112 pazienti disosmici per la consistenza interna e 61 per l’affidabilità test-retest), generazione di dati normativi (303 soggetti normosmici), analisi di validità (comparazione dei punteggi Brief-IT-QOD di pazienti e controlli e correlazione con valutazione olfattoria psicofisica TDI e punteggio SNOT-22), analisi di responsività (10 pazienti disosmici con rinosinusite cronica poliposica prima e dopo terapia biologica), e determinazione di valori soglia.
Risultati: Tutti i soggetti hanno completato il Brief-IT-QOD. Consistenza interna (α > 0,70) e affidabilità test-retest (ICC > 0,7) erano soddisfacenti per entrambe le sottoscale del questionario. In entrambe le componenti è stata rilevata una differenza significativa (p < 0,05) fra individui disosmici e normosmici. Sono emerse correlazioni significative fra i punteggi delle sottoscale e i punteggi TDI e SNOT-22. I punteggi al Brief-IT-QOD erano significativamente più alti prima della terapia con farmaco biologico.
Conclusioni: Il Brief-IT-QOD è affidabile, valido, responsivo ai cambiamenti nella qualità di vita e raccomandato per pratica clinica e ricerca.
Keywords: olfaction disorders; quality of life; questionnaire.
Copyright © 2023 Società Italiana di Otorinolaringoiatria e Chirurgia Cervico-Facciale, Rome, Italy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validity and reliability of the Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders for Italian-speaking patients with olfactory dysfunction.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2024 Feb;44(1):42-51. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-N2736. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2024. PMID: 38420720 Free PMC article.
-
Olfaction-associated quality of life: Polish adaptation and validation of a Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders (QOD-PL) in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2024 Feb;33(2):143-150. doi: 10.17219/acem/169978. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 37676099
-
Reliability and validity of the Arabic version of the brief version of the Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024 May 9;9(3):e1252. doi: 10.1002/lio2.1252. eCollection 2024 Jun. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38736942 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory Outcomes after Endoscopic Sinus Surgery for Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Meta-analysis.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016 Dec;155(6):936-948. doi: 10.1177/0194599816664879. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2016. PMID: 27576679 Review.
-
[Detection of disorders of the chemical senses-assessment of state of health by those affected].HNO. 2023 Sep;71(9):566-571. doi: 10.1007/s00106-023-01345-3. Epub 2023 Aug 3. HNO. 2023. PMID: 37535151 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Validity and reliability of the Questionnaire of Olfactory Disorders for Italian-speaking patients with olfactory dysfunction.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2024 Feb;44(1):42-51. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-N2736. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2024. PMID: 38420720 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hummel T, Whitcroft KL, Andrews P, et al. . Position paper on olfactory dysfunction. Rhinol (Suppl.) 2017;54:1-30. https://doi.org/10.4193/Rhino16.248 10.4193/Rhino16.248 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Croy I, Nordin S, Hummel T. Olfactory disorders and quality of life – an updated review. Chem Senses 2014;39:185-194. https://doi.org/10.1093/chemse/bjt072 10.1093/chemse/bjt072 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wilson RS, Yu L, Bennett DA. Odor identification and mortality in old age. Chem Senses 2011;36:63-67. https://doi.org/10.1093/chemse/bjq098 10.1093/chemse/bjq098 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frasnelli J, Hummel T. Olfactory dysfunction and daily life. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2005;262:231-235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-004-0796-y 10.1007/s00405-004-0796-y - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yang D, Wang J, Ni D, et al. . Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the questionnaire of olfactory disorders (QOD) when used with patients having olfactory dysfunction. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2016;273:3255-3261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3869-1 10.1007/s00405-015-3869-1 - DOI - PubMed

