Reprogramming of three-dimensional chromatin organization in the early embryo
- PMID: 37224641
- PMCID: PMC10524315
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2023.102613
Reprogramming of three-dimensional chromatin organization in the early embryo
Abstract
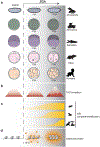
Chromatin organization within the three-dimensional (3D) nuclear space is important for proper gene expression and developmental programming. This organization is established during the dramatic reprogramming that occurs in early embryonic development. Thus, the early embryo is an ideal model for examining the formation and dynamics of 3D chromatin structure. Advances in high-resolution microscopy and single-nucleus genomic analyses have provided fundamental insights into the mechanisms driving genome organization in the early embryo. Here, we highlight recent findings describing the dynamics and driving mechanisms for establishing 3D chromatin organization and discuss the role such organization has on gene regulation in early embryonic development.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Gizzi AMC, Cattoni DI, Fiche J-B, Espinola SM, Gurgo J, Messina O, Houbron C, Ogiyama Y, Papadopoulos GL, Cavalli G, et al.: Microscopy-Based Chromosome Conformation Capture Enables Simultaneous Visualization of Genome Organization and Transcription in Intact Organisms. Mol Cell 2019, 74:212–222.e5. - PubMed
-
- Hug CB, Grimaldi AG, Kruse K, Vaquerizas JM: Chromatin Architecture Emerges during Zygotic Genome Activation Independent of Transcription. Cell 2017, 169:216–228.e19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

