Acute respiratory failure-related excess mortality in pediatric sepsis
- PMID: 37225415
- PMCID: PMC10953703
- DOI: 10.1136/thorax-2022-219961
Acute respiratory failure-related excess mortality in pediatric sepsis
Abstract
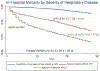
Excess mortality risk imparted by acute respiratory failure in children is unknown. We determined excess mortality risk associated with mechanically ventilated acute respiratory failure in pediatric sepsis. Novel ICD10-based algorithms were derived and validated to identify a surrogate for acute respiratory distress syndrome to calculate excess mortality risk. Algorithm-identified ARDS was identified with specificity of 96.7% (CI 93.0 - 98.9) and sensitivity of 70.5% (CI 44.0 - 89.7). Excess risk of mortality for ARDS was 24.4% (CI 22.9 - 26.2). Development of ARDS requiring mechanical ventilation imparts modest excess risk of mortality in septic children.
Keywords: ARDS; Critical Care; Paediatric Lung Disaese.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
