Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Levels are Associated with Vascular Smooth Muscle Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 37225519
- PMCID: PMC10703563
- DOI: 10.5551/jat.64000
Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Levels are Associated with Vascular Smooth Muscle Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
Aim: Increased level of serum fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) is a hallmark of abnormal phosphate metabolism in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is recently shown to be associated with the risk of cardiovascular disease even in those without CKD. This study investigated the association between serum FGF23 levels and vascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study involving 283 Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. Flow-mediated dilatation (FMD) and nitroglycerin-mediated dilatation (NMD) of the brachial artery were measured via ultrasonography to evaluate vascular endothelial and smooth muscle functions, respectively. Serum intact FGF23 levels were determined via a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
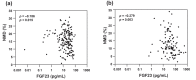
Results: The median values of FMD, NMD, and serum FGF23 were 6.0%, 14.0%, and 27.3 pg/mL, respectively. The serum FGF23 levels were inversely associated with NMD but not with FMD, and the association was independent of atherosclerotic risk factors, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and serum phosphate levels. Furthermore, the relationship between serum FGF23 levels and NMD was modified by kidney function, which was pronounced in subjects with normal kidney function (eGFR ≥ 60 mL/min/1.73 m2).
Conclusion: Serum FGF23 levels are independently and inversely associated with NMD in patients with type 2 diabetes, particularly in those with normal kidney function. Our results indicate that FGF23 is involved in vascular smooth muscle dysfunction and that increased serum levels of FGF23 may serve as a novel biomarker for vascular smooth muscle dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Fibroblast Growth Factor 23; Flow-Mediated Dilatation; Nitroglycerin-Mediated Dilatation; Type 2 Diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phosphate, fibroblast growth factor 23 and retinopathy in chronic kidney disease: the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort Study.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015 Sep;30(9):1534-41. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv123. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25910495 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor 23 and kidney function in patients with type 1 diabetes.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 9;17(9):e0274182. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274182. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36084108 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated serum fibroblast growth factor 23 levels as an indicator of lower extremity atherosclerotic disease in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017 Jun 15;16(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0559-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017. PMID: 28619026 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of different phosphate binders on fibroblast growth factor 23 levels in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Ann Palliat Med. 2022 Apr;11(4):1264-1277. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1943. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Ann Palliat Med. 2022. PMID: 34775773
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: a Bitter-Sweet Symphony.Curr Diab Rep. 2020 Aug 28;20(10):50. doi: 10.1007/s11892-020-01335-7. Curr Diab Rep. 2020. PMID: 32857288 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fibroblast Growth Factors in Cardiovascular Disease.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024 Nov 1;31(11):1496-1511. doi: 10.5551/jat.RV22025. Epub 2024 Aug 22. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024. PMID: 39168622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of xanthine oxidoreductase inhibitor use with insulin secretory capacity in patients with type 2 diabetes.J Diabetes Investig. 2024 Oct;15(10):1500-1509. doi: 10.1111/jdi.14279. Epub 2024 Jul 30. J Diabetes Investig. 2024. PMID: 39078414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Imanishi Y, Inaba M, Nakatsuka K, Nagasue K, Okuno S, Yoshihara A, Miura M, Miyauchi A, Kobayashi K, Miki T, Shoji T, Ishimura E and Nishizawa Y: FGF-23 in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. Kidney Int, 2004; 65: 1943-1946 - PubMed
-
- Isakova T, Wahl P, Vargas GS, Gutiérrez OM, Scialla J, Xie H, Appleby D, Nessel L, Bellovich K, Chen J, Hamm L, Gadegbeku C, Horwitz E, Townsend RR, Anderson CA, Lash JP, Hsu CY, Leonard MB and Wolf M: Fibroblast growth factor 23 is elevated before parathyroid hormone and phosphate in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int, 2011; 79: 1370-1378 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

