Mechanical Ventilation during ECMO: Best Practices
- PMID: 37225656
- PMCID: PMC10208991
- DOI: 10.4187/respcare.10908
Mechanical Ventilation during ECMO: Best Practices
Abstract
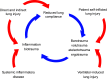
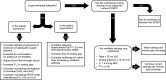
Adults and children who require extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for respiratory failure remain at risk for ongoing lung injury if ventilator management is not optimized. This review serves as a guide to assist the bedside clinician in ventilator titration for patients on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, with a focus on lung-protective strategies. Existing data and guidelines for extracorporeal membrane oxygenation ventilator management are reviewed, including non-conventional ventilation modes and adjunct therapies.
Keywords: Mechanical ventilation; acute respiratory distress syndrome; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; ventilator induced lung injury.
Copyright © 2023 by Daedalus Enterprises.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Peek GJ, Mugford M, Tiruvoipati R, Wilson A, Allen E, Thalanany MM, et al. ; CESAR trial collaboration. Efficacy and economic assessment of conventional ventilatory support versus extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe adult respiratory failure (CESAR): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009;374(9698):1351-1363. - PubMed
-
- Noah MA, Peek GJ, Finney SJ, Griffiths MJ, Harrison DA, Grieve R, et al. . Referral to an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation center and mortality among patients with severe 2009 influenza A(H1N1). JAMA 2011;306(15):1659-1668. - PubMed
-
- Zabrocki LA, Brogan TV, Statler KD, Poss WB, Rollins MD, Bratton SL. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for pediatric respiratory failure: survival and predictors of mortality. Crit Care Med 2011;39(2):364-370. - PubMed
-
- ECMO Registry of the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO); Ann Arbor, Michigan; January 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources