Integrating intracellular and extracellular proteomic profiling for in-depth investigations of cellular communication in a model of prostate cancer
- PMID: 37226375
- PMCID: PMC10667563
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.202200287
Integrating intracellular and extracellular proteomic profiling for in-depth investigations of cellular communication in a model of prostate cancer
Abstract
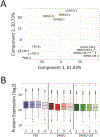
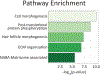
Cellular communication is essential for cell-cell interactions, maintaining homeostasis and progression of certain disease states. While many studies examine extracellular proteins, the holistic extracellular proteome is often left uncaptured, leaving gaps in our understanding of how all extracellular proteins may impact communication and interaction. We used a cellular-based proteomics approach to more holistically profile both the intracellular and extracellular proteome of prostate cancer. Our workflow was generated in such a manner that multiple experimental conditions can be observed with the opportunity for high throughput integration. Additionally, this workflow is not limited to a proteomic aspect, as metabolomic and lipidomic studies can be integrated for a multi-omics workflow. Our analysis showed coverage of over 8000 proteins while also garnering insights into cellular communication in the context of prostate cancer development and progression. Identified proteins covered a variety of cellular processes and pathways, allowing for the investigation of multiple aspects into cellular biology. This workflow demonstrates advantages for integrating intra- and extracellular proteomic analyses as well as potential for multi-omics researchers. This approach possesses great value for future investigations into the systems biology aspects of disease development and progression.
Keywords: extracellular profiling; intracellular profiling; network analysis; prostate cancer; proteomic analysis.
© 2023 The Authors. Proteomics published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Figures
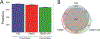

References
-
- Simeone P, Bologna G, Lanuti P, Pierdomenico L, Guagnano MT, Pieragostino D, … Mariani-Costantini R (2020). Extracellular Vesicles as Signaling Mediators and Disease Biomarkers across Biological Barriers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(7), 2514. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072514 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yu Q, Zhong X, Chen B, Feng Y, Ma M, Diamond CA, … Li L (2020). Isobaric Labeling Strategy Utilizing 4-Plex N,N-Dimethyl Leucine (DiLeu) Tags Reveals Proteomic Changes Induced by Chemotherapy in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Children with B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Journal of Proteome Research, 19(7), 2606–2616. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00291 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hao L, Thomas S, Greer T, Vezina CM, Bajpai S, Ashok A, … Ricke WA (2019). Quantitative proteomic analysis of a genetically induced prostate inflammation mouse model via custom 4-plex DiLeu isobaric labeling. American Journal of Physiology - Renal Physiology, 316(6), F1236–F1243. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00387.2018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10 OD025084/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10OD025084/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK127081/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG052324/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DK104310/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10RR029531/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG065728/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21AG065728/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- S10OD028473/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD028473/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG052324/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR029531/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG078794/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK071801/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- RF1AG052324/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK071801/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54DK104310/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG078794/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK131175/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

