Effects of chronic sleep restriction on the neuro-phenotypes of Ctnnd2 knockout mice
- PMID: 37226399
- PMCID: PMC10338785
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.3075
Effects of chronic sleep restriction on the neuro-phenotypes of Ctnnd2 knockout mice
Abstract
Introduction: Sleep abnormalities are highly correlated with neurodevelopmental disorders, such as intellectual disability, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and autism spectrum disorders (ASD). The severity of behavioral abnormalities is correlated with the presence of sleep abnormalities. Based on previous research, we investigated that Ctnnd2 gene deletion in mice lead to ASD-like behaviors and cognitive defects. Given the importance of sleep in individuals with ASD, this study aimed to determine the effects of chronic sleep restriction (SR) on wild-type (WT) mice and on Ctnnd2 deletion-induced, neurologically related phenotypes in mice.
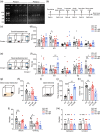
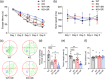
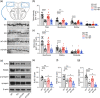
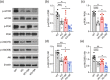
Method: WT and Ctnnd2 knockout (KO) mice were both subjected to manual SR (5 h per day) for 21 consecutively days separately, then we compared neurologically related phenotypes of WT mice, WT mice subjected to SR, KO mice, and KO mice subjected to SR using a three-chamber assay, direct social interaction test, open-field test, Morris water maze, Golgi staining, and Western blotting.
Results: The effects of SR on WT and KO mice were different. After SR, social ability and cognition were impaired in both WT and KO mice. Repetitive behaviors were increased, and exploration abilities were decreased in KO mice but not in WT mice. Moreover, SR reduced the density and area of mushroom-type dendritic spines in WT rather than KO mice. Finally, the PI3K/Akt-mTOR pathway was found to be involved in the effects induced by SR-impaired phenotypes in WT and KO mice.
Conclusion: Overall, results of the present study may have implications for the role of disrupted sleep in patients with CTNND2 gene-related autism and the evolution of neurodevelopmental disorders.
Keywords: Ctnnd2; autism; cognition; dendritic spines; sleep restriction; synapse.
© 2023 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Arikkath, J. , Peng, I. F. , Ng, Y. G. , Israely, I. , Liu, X. , Ullian, E. M. , & Reichardt, L. F. (2009). Delta‐catenin regulates spine and synapse morphogenesis and function in hippocampal neurons during development. Journal of Neuroscience, 29(17), 5435–5442. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0835-09.2009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

