The role of bioimpedance analysis in overweight and obese patients with acute heart failure: a pilot study
- PMID: 37226407
- PMCID: PMC10375164
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.14398
The role of bioimpedance analysis in overweight and obese patients with acute heart failure: a pilot study
Abstract
Aims: Residual congestion at the time of hospital discharge is an important readmission risk factor, and its detection with physical examination and usual diagnostic techniques have strong limitations in overweight and obese patients. New tools like bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) could help to determine when euvolaemia is reached. The aim of this study was to investigate the usefulness of BIA in management of heart failure (HF) in overweight and obese patients.
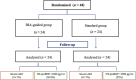
Methods and results: Our study is a single-centre, single-blind, randomized controlled trial that included 48 overweight and obese patients admitted for acute HF. The study population was randomized into two arms: BIA-guided group and standard care. Serum electrolytes, kidney function, and natriuretic peptides were followed up during their hospital stay and at 90 days after discharge. The primary endpoint was development of severe acute kidney injury (AKI) defined as an increase in serum creatinine by >0.5 mg/dL during hospitalization, and the main secondary endpoint was the reduction of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels during hospitalization and within 90 days after discharge. The BIA-guided group showed a remarkable lower incidence of severe AKI, although no significant differences were found (41.4% vs. 16.7%; P = 0.057). The proportion of patients who achieved levels of NT-proBNP < 1000 pg/mL at 90 days was significantly higher in the BIA-guided group than in the standard group (58.8% vs. 25%; P = 0.049). No differences were observed in the incidence of adverse outcomes at 90 days.
Conclusions: Among overweight and obese patients with HF, BIA reduces NT-proBNP levels at 90 days compared with standard care. In addition, there is a trend towards lower incidence of AKI in the BIA-guided group. Although more studies are required, BIA could be a useful tool in decompensated HF management in overweight and obese patients.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Bioimpedance analysis; Heart failure; Natriuretic peptides; Obesity.
© 2023 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Savarese G, Becher PM. Global burden of heart failure: a comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc Res. 2022; 118: 3272–3287. - PubMed
-
- Goldgrab D, Balakumaran K. Updates in heart failure 30‐day readmission prevention. Heart Fail Rev. 2019; 24: 177–187. - PubMed
-
- Lala A, McNulty SE. Relief and recurrence of congestion during and after hospitalization for acute heart failure: insights from Diuretic Optimization Strategy Evaluation in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (DOSE‐AHF) and Cardiorenal Rescue Study in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (CARESS‐HF). Circ Heart Fail. 2015; 8: 741–748. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chakko S, Woska D. Clinical, radiographic, and hemodynamic correlations in chronic congestive heart failure: conflicting results may lead to inappropriate care. Am J Med. 1991; 90: 353–359. - PubMed
-
- Sergy G, Bussolotto M. Accuracy of bioelectrical impedance analysis in estimation of extracellular space in healthy subject and in fluid retention states. Ann Nutr Metab. 1994; 38: 158–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

