Randomized, Phase II study of pemetrexed plus bevacizumab versus pemetrexed alone after treatment with cisplatin, pemetrexed, and bevacizumab in advanced non-squamous, non-small cell lung cancer: TORG (thoracic oncology research group) 1321
- PMID: 37226421
- PMCID: PMC10417045
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.6135
Randomized, Phase II study of pemetrexed plus bevacizumab versus pemetrexed alone after treatment with cisplatin, pemetrexed, and bevacizumab in advanced non-squamous, non-small cell lung cancer: TORG (thoracic oncology research group) 1321
Abstract
Introduction: Cisplatin plus pemetrexed followed by pemetrexed is an efficacious platinum combination regimen for advanced non-squamous, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Data regarding the addition of bevacizumab, especially in maintenance treatment, are insufficient.
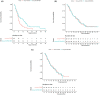
Methods: Eligibility criteria included: no prior chemotherapy; advanced, non-squamous, NSCLC; performance status ≤1; and epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-negative. Patients (N = 108) received induction chemotherapy with cisplatin, pemetrexed, and bevacizumab every 3 weeks for four cycles, and tumor response was needed to confirm four-week response duration. Patients with at least stable disease were randomized to pemetrexed/bevacizumab or pemetrexed alone. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS) after induction chemotherapy. Myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) counts of peripheral blood samples were also analyzed.
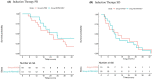
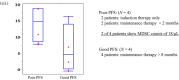
Results: Thirty-five patients each were randomized to the pemetrexed/bevacizumab group and the pemetrexed alone group. PFS was significantly better in the pemetrexed/bevacizumab group than in the pemetrexed alone group (7.0 vs. 5.4 months, hazard ratio: 0.56 [0.34-0.93], log-rank p = 0.023). In patients with partial response to induction therapy, median overall survival was 23.3 months in the pemetrexed alone group and 29.6 months in the pemetrexed/bevacizumab group (log-rank p = 0.077). Pretreatment monocytic (M)-MDSC counts tended to be greater in the pemetrexed/bevacizumab group with poor PFS than in those with good PFS (p = 0.0724).
Conclusions: Addition of bevacizumab to pemetrexed as maintenance therapy prolonged PFS in patients with untreated, advanced, non-squamous NSCLC. Furthermore, an early response to induction therapy and pretreatment M-MDSC counts may be related to the survival benefit of the addition of bevacizumab to the combination of cisplatin and pemetrexed.
Keywords: Phase II study; advanced; bevacizumab maintenance therapy; cisplatin; non-small cell lung cancer; non-squamous; pemetrexed; randomized.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Maintenance therapy with pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care after induction therapy with pemetrexed plus cisplatin for advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (PARAMOUNT): a double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial.Lancet Oncol. 2012 Mar;13(3):247-55. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70063-3. Epub 2012 Feb 16. Lancet Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22341744 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II study of cisplatin/pemetrexed combined with bevacizumab followed by pemetrexed/bevacizumab maintenance therapy in patients with EGFR-wild advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018 Jun;81(6):1043-1050. doi: 10.1007/s00280-018-3573-0. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29644460 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized phase III trial of maintenance bevacizumab with or without pemetrexed after first-line induction with bevacizumab, cisplatin, and pemetrexed in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer: AVAPERL (MO22089).J Clin Oncol. 2013 Aug 20;31(24):3004-11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.42.3749. Epub 2013 Jul 8. J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23835708 Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy and toxicity of maintenance therapy with bevacizumab plus pemetrexed versus bevacizumab/pemetrexed alone for stage IIIB/IV nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022 Feb;47(2):157-167. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13534. Epub 2021 Oct 6. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022. PMID: 34617297 Review.
-
Maintenance treatment of combination with bevacizumab vs single agent for advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Aug 6;100(31):e26862. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026862. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34397863 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advances in Predictive Biomarkers for Anti-Angiogenic Therapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancer Control. 2024 Jan-Dec;31:10732748241270589. doi: 10.1177/10732748241270589. Cancer Control. 2024. PMID: 39192835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between increased proteinuria induced by Bevacizumab, Ramucirumab, and Aflibercept and the risk of renal impairment and failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Clin Oncol. 2025 Jul 5. doi: 10.1007/s10147-025-02819-w. Online ahead of print. Int J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40616772 Review.
References
-
- Rebecca L, Siegel MPH, Kimberly D, Miller MPH, Ahmedin Jemal DVM. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7‐30. - PubMed
-
- Grilli R, Oxman AD, Julian JA. Chemotherapy for advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer: how much benefit is enough? J Clin Oncol. 1993;11:1866‐1872. - PubMed
-
- Souquet PJ, Chauvin F, Boissel JP, et al. Polychemotherapy in advanced non small cell lung cancer: a meta‐analysis. Lancet. 1993;342:19‐21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

