A Pilot Validation Study Comparing Fluorescence-Imitating Brightfield Imaging, A Slide-Free Imaging Method, With Standard Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Hematoxylin-Eosin-Stained Tissue Section Histology for Primary Surgical Pathology Diagnosis
- PMID: 37226827
- PMCID: PMC12054848
- DOI: 10.5858/arpa.2022-0432-OA
A Pilot Validation Study Comparing Fluorescence-Imitating Brightfield Imaging, A Slide-Free Imaging Method, With Standard Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Hematoxylin-Eosin-Stained Tissue Section Histology for Primary Surgical Pathology Diagnosis
Abstract
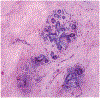
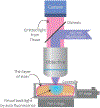
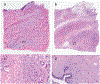
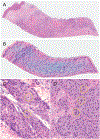
Context.—: Digital pathology using whole slide images has been recently approved to support primary diagnosis in clinical surgical pathology practices. Here we describe a novel imaging method, fluorescence-imitating brightfield imaging, that can capture the surface of fresh tissue without requiring prior fixation, paraffin embedding, tissue sectioning, or staining.
Objective.—: To compare the ability of pathologists to evaluate direct-to-digital images with standard pathology preparations.
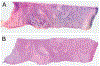
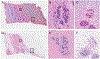
Design.—: One hundred surgical pathology samples were obtained. Samples were first digitally imaged, then processed for standard histologic examination on 4-μm hematoxylin-eosin-stained sections and digitally scanned. The resulting digital images from both digital and standard scan sets were viewed by each of 4 reading pathologists. The data set consisted of 100 reference diagnoses and 800 study pathologist reads. Each study read was compared to the reference diagnosis, and also compared to that reader's diagnosis across both modalities.
Results.—: The overall agreement rate, across 800 reads, was 97.9%. This consisted of 400 digital reads at 97.0% versus reference and 400 standard reads versus reference at 98.8%. Minor discordances (defined as alternative diagnoses without clinical treatment or outcome implications) were 6.1% overall, 7.2% for digital, and 5.0% for standard.
Conclusions.—: Pathologists can provide accurate diagnoses from fluorescence-imitating brightfield imaging slide-free images. Concordance and discordance rates are similar to published rates for comparisons of whole slide imaging to standard light microscopy of glass slides for primary diagnosis. It may be possible, therefore, to develop a slide-free, nondestructive approach for primary pathology diagnosis.
© 2024 College of American Pathologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Borowsky, Levenson, and Fereidouni are cofounders of Histolix Inc; Gown is a consultant to Histolix Inc; and Morningstar was a paid full-time employee of Histolix Inc for part of the time of the study. Fleury has a financial interest in a capital group that has invested in Histolix. The other authors have no relevant financial interest in the products or companies described in this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Current Landscape of Advanced Imaging Tools for Pathology Diagnostics.Mod Pathol. 2024 Apr;37(4):100443. doi: 10.1016/j.modpat.2024.100443. Epub 2024 Feb 3. Mod Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38311312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-institutional comparison of whole slide digital imaging and optical microscopy for interpretation of hematoxylin-eosin-stained breast tissue sections.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013 Dec;137(12):1733-9. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2012-0437-OA. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013. PMID: 23947655
-
Comparing Accuracy of Helicobacter pylori Identification Using Traditional Hematoxylin and Eosin-Stained Glass Slides With Digital Whole Slide Imaging.Lab Invest. 2024 Jan;104(1):100262. doi: 10.1016/j.labinv.2023.100262. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Lab Invest. 2024. PMID: 37839639
-
Whole slide imaging equivalency and efficiency study: experience at a large academic center.Mod Pathol. 2019 Jul;32(7):916-928. doi: 10.1038/s41379-019-0205-0. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Mod Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30778169
-
Whole slide imaging: uses and limitations for surgical pathology and teaching.Biotech Histochem. 2015 Jul;90(5):321-30. doi: 10.3109/10520295.2015.1033463. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Biotech Histochem. 2015. PMID: 25901738 Review.
Cited by
-
GigaFIBI; Rapid, Large-format Histology-resolution Imaging for Intraoperative Assessment of Breast Lumpectomy Margins.Biomed Opt. 2024 Apr;2024:MS1A.2. doi: 10.1364/MICROSCOPY.2024.MS1A.2. Biomed Opt. 2024. PMID: 40331024 Free PMC article.
-
Current Landscape of Advanced Imaging Tools for Pathology Diagnostics.Mod Pathol. 2024 Apr;37(4):100443. doi: 10.1016/j.modpat.2024.100443. Epub 2024 Feb 3. Mod Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38311312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Digital pathology systems enabling quality patient care.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2023 Nov;62(11):685-697. doi: 10.1002/gcc.23192. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37458325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utility of fluorescence imitating brightfield imaging microscopy for the diagnosis of feline chronic enteropathy.Vet Pathol. 2023 Jan;60(1):52-59. doi: 10.1177/03009858221131363. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Vet Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36286074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cardiff RD, Gregg JP, Miller JW, Axelrod DE, Borowsky AD. Histopathology as a predictive biomarker: strengths and limitations. J Nutr. 2006;136(10):2673S–5S. - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA news release: FDA allows marketing of first whole slide imaging system for digital pathology; 2017. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-allows-marketing.... Accessed February 10, 2023.
-
- Borowsky AD, Glassy EF, Wallace WD, et al. Digital whole slide imaging compared with light microscopy for primary diagnosis in surgical pathology. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2020;144(10):1245–1253. - PubMed

