INMUNOCAT study: The impact of molecular diagnosis on immunotherapy prescription in pollen polysensitized patients from Catalonia
- PMID: 37227418
- PMCID: PMC10154984
- DOI: 10.1002/clt2.12246
INMUNOCAT study: The impact of molecular diagnosis on immunotherapy prescription in pollen polysensitized patients from Catalonia
Abstract
Background: Recognition of specific allergens triggering immune response is key for the appropriate prescription of allergen-specific immunotherapy (SIT). This study aimed at evaluating the impact of using the commercially available microarray ImmunoCAPTM ISAC 112 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) on the etiological diagnosis and SIT prescription compared to the conventional diagnostic methods in patients with allergic rhinitis/rhinoconjunctivitis and/or asthma.
Methods: 300 patients with respiratory allergic disease, sensitized to three or more pollen aeroallergens from different species, as assessed by a skin prick test (SPT) and specific IgE assays (sIgE), were included in this multicentric, prospective observational study. SPT and a blood test were performed to all patients. Total serum IgE and sIgE (ImmunoCAPTM) for allergens found positive in the SPT and sIgE allergen components (ImmunoCAPTM ISAC 112) were measured.
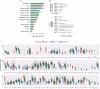
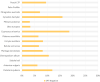
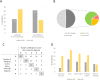
Results: According to SPT results, the most prevalent pollen sensitizers in our population were Olea europaea followed by grass, Platanus acerifolia and Parietaria judaica. The molecular diagnosis (MD) revealed Ole e 1 as the most prevalent pollen sensitizer, followed by Cup a 1, Phl p 1, Cyn d 1, Par j 2, Pla a 1, 2, and 3 and Phl p 5. Immunotherapy prescription changed, due to MD testing, in 51% of the cases, with an increase of prescription of SIT from 39% to 65%.
Conclusion: The identification of the allergen eliciting the respiratory disease is essential for a correct immunotherapy prescription. The advances in allergen characterization using methods, such as the commercial microarray ImmunoCAPTM ISAC 112, can help clinicians to improve SIT prescription.
Keywords: asthma; change; immunotherapy; molecular diagnosis; personalized medicine; pollen polysensitized patients; rhinitis; rhinoconjunctivitis.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Allergy published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
Mercè Tena works as Scientific Liaison at Thermo Fisher Scientific. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- SEIAC . Pólenes alergénicos en España; 2021. accessed 20 Jun2022. https://www.polenes.com/es/polenes‐alergenicos
-
- Pereira C, Valero A, Loureiro C, et al. Iberian study of aeroallergens sensitization in allergic rhinitis. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;38:186‐194. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

