A pilot randomised trial comparing individualised physiotherapy versus shockwave therapy for proximal hamstring tendinopathy: a protocol
- PMID: 37227516
- PMCID: PMC10212870
- DOI: 10.1186/s40634-023-00615-x
A pilot randomised trial comparing individualised physiotherapy versus shockwave therapy for proximal hamstring tendinopathy: a protocol
Abstract
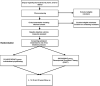
Purpose: Proximal hamstring tendinopathy (PHT) presents as localised lower buttock pain with tasks such as squatting and sitting. It is a condition that occurs at all ages and levels of sporting participation and can cause disability with sport, work, and activities of daily living. This paper details a pilot trial protocol for investigating the effectiveness of individualised physiotherapy compared to extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) on pain and strength in people with PHT.
Methods: The study is an assessor-blinded, pilot randomised controlled trial (RCT). One hundred participants with PHT will be recruited from the local community and sporting clubs. Participants will be randomised to receive six sessions of either individualised physiotherapy or ESWT, with both groups also receiving standardised education and advice. Primary outcomes will be global rating of change on a 7-point Likert scale, and the Victorian Institute of Sport-Hamstring (VISA-H) scale, measured at 0, 4, 12, 26 and 52 weeks. Secondary outcomes will include sitting tolerance, the modified Physical Activity Level Scale, eccentric hamstring strength, modified Tampa scale for kinesiophobia, the Örebro Musculoskeletal Pain Screening Questionnaire Short Form (ÖMPSQ-SF), Numerical Pain Rating Scale (NPRS) for average and worst pain, participant adherence, the Pain Catastrophizing scale, satisfaction scores, and quality of life. Data will be analysed on an intention to treat basis, with between-group effects estimated using linear mixed models for continuous data and Mann Whitney U tests for ordinal data.
Conclusions: This pilot RCT will compare individualised physiotherapy versus ESWT for PHT. The trial will determine feasibility and estimated treatment effects to inform a definitive trial in the future.
Trial registration: The trial has been prospectively registered with the Australia & New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (ACTRN12621000846820), registered 1 July 2021, https://www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?id=373085.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There are no competing or financial interests for the principal investigators for this trial.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Randomised, cross-over trial on the effect of isotonic and isometric exercise on pain and strength in proximal hamstring tendinopathy: trial protocol.BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2021 Jan 5;7(1):e000954. doi: 10.1136/bmjsem-2020-000954. eCollection 2021. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2021. PMID: 33456785 Free PMC article.
-
Specific treatment of problems of the spine (STOPS): design of a randomised controlled trial comparing specific physiotherapy versus advice for people with subacute low back disorders.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011 May 20;12:104. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-12-104. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011. PMID: 21599941 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A comparison of isometric, isotonic concentric and isotonic eccentric exercises in the physiotherapy management of subacromial pain syndrome/rotator cuff tendinopathy: study protocol for a pilot randomised controlled trial.Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2017 Nov 14;3:45. doi: 10.1186/s40814-017-0190-3. eCollection 2017. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2017. PMID: 29163981 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of non-surgical management in rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy (the effect trial): protocol for a randomised clinical trial.BMJ Open. 2024 Jan 4;14(1):e074949. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-074949. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38176875 Free PMC article.
-
Surgery for patellar tendinopathy (jumper's knee).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 23;9(9):CD013034. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013034.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31546279 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regenerative Medicine in Orthopedic Surgery: Expanding Our Toolbox.Cureus. 2024 Sep 2;16(9):e68487. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68487. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39364457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and future advances in practice: tendinopathies of the hip.Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2024 Apr 10;8(2):rkae022. doi: 10.1093/rap/rkae022. eCollection 2024. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2024. PMID: 38601140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Proximal Hamstring Tendinopathy with Individualized Physiotherapy: A Clinical Commentary.Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2025 Jun 2;20(6):892-910. doi: 10.26603/001c.138308. eCollection 2025. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2025. PMID: 40469642 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous