Roles of ApoE4 on the Pathogenesis in Alzheimer's Disease and the Potential Therapeutic Approaches
- PMID: 37227619
- PMCID: PMC10211310
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-023-01365-1
Roles of ApoE4 on the Pathogenesis in Alzheimer's Disease and the Potential Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
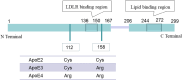
The Apolipoprotein E ε4 (ApoE ε4) allele, encoding ApoE4, is the strongest genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD). Emerging epidemiological evidence indicated that ApoE4 contributes to AD through influencing β-amyloid (Aβ) deposition and clearance. However, the molecular mechanisms of ApoE4 involved in AD pathogenesis remains unclear. Here, we introduced the structure and functions of ApoE isoforms, and then we reviewed the potential mechanisms of ApoE4 in the AD pathogenesis, including the effect of ApoE4 on Aβ pathology, and tau phosphorylation, oxidative stress; synaptic function, cholesterol transport, and mitochondrial dysfunction; sleep disturbances and cerebrovascular integrity in the AD brains. Furthermore, we discussed the available strategies for AD treatments that target to ApoE4. In general, this review overviews the potential roles of ApoE4 in the AD development and suggests some therapeutic approaches for AD. ApoE4 is genetic risk of AD. ApoE4 is involved in the AD pathogenesis. Aβ deposition, NFT, oxidative stress, abnormal cholesterol, mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation could be observed in the brains with ApoE4. Targeting the interaction of ApoE4 with the AD pathology is available strategy for AD treatments.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease (AD); Apolipoprotein E4 (ApoE4); Therapy; β-Amyloid (Aβ).
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Unraveling APOE4's Role in Alzheimer's Disease: Pathologies and Therapeutic Strategies.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2025;26(4):259-281. doi: 10.2174/0113892037326839241014054430. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2025. PMID: 39722484 Review.
-
APOE and Alzheimer's Disease: Evidence Mounts that Targeting APOE4 may Combat Alzheimer's Pathogenesis.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Apr;56(4):2450-2465. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1237-z. Epub 2018 Jul 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30032423 Review.
-
ApoE4 reduction: An emerging and promising therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Aging. 2022 Jul;115:20-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2022.03.011. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Neurobiol Aging. 2022. PMID: 35453035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer's Disease: Focus on Synaptic Function and Therapeutic Strategy.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Mar;62(3):3040-3052. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04449-1. Epub 2024 Aug 31. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39214953 Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E, especially apolipoprotein E4, increases the oligomerization of amyloid β peptide.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 24;32(43):15181-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1542-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23100439 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Apolipoprotein E (APOE) and Alzheimer's disease risk in a Ugandan population: A pilot case-control study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 May 9;104(19):e42407. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042407. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40355218 Free PMC article.
-
DNA tetrahedron-based dual-signal fluorescence detection of apoE4 gene sites on a microplate reader.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Apr 26;191(5):288. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06365-6. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38671226
-
Targeting Ferroptosis/Nrf2 Pathway Ameliorates AlCl3-Induced Alzheimer's Disease in Rats: Neuroprotective Effect of Morin Hydrate, Zeolite Clinoptilolite, and Physical Plus Mental Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 31;26(3):1260. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031260. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39941034 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Roles of Apolipoprotein E4 in Oxidative Lipid Metabolism and Ferroptosis During the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2024 Jul 3;74(3):62. doi: 10.1007/s12031-024-02224-4. J Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38958788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of apolipoprotein E, type ∊4 allele on Alzheimer's disease pathological biomarkers: a comprehensive post-mortem pilot-analysis.PLoS One. 2025 Feb 6;20(2):e0303486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303486. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39913635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilar-Pineda JA, Paco-Coralla SG, Febres-Molina C, Gamero-Begazo PL, Shrivastava P, Vera-López KJ, Davila-Del-Carpio G, López CP, Gómez B, Lino Cardenas CL (2022) In silico analysis of the antagonist effect of enoxaparin on the ApoE4-amyloid-beta (Aβ) complex at different pH conditions. Biomolecules. 10.3390/biom12040499 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arold S, Sullivan P, Bilousova T, Teng E, Miller CA, Poon WW, Vinters HV, Cornwell LB, Saing T, Cole GM, Gylys KH (2012) Apolipoprotein E level and cholesterol are associated with reduced synaptic amyloid beta in Alzheimer’s disease and apoE TR mouse cortex. Acta Neuropathol 123 (1):39–52. 10.1007/s00401-011-0892-1 - PMC - PubMed
-
- As Association (2020) 2020 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimer's Dementia. 10.1002/alz.12068 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

