Determinants of neuropsychiatric flares in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from five phase III trials of belimumab
- PMID: 37228034
- PMCID: PMC10907808
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead249
Determinants of neuropsychiatric flares in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from five phase III trials of belimumab
Abstract
Objective: To identify determinants of neuropsychiatric (NP) flares in patients with SLE treated for active SLE yet no ongoing severe NPSLE with non-biologic standard therapy plus belimumab or placebo.
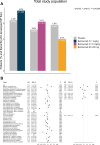
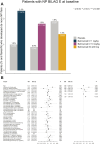
Methods: We analysed data from five phase III trials (BLISS-52, BLISS-76, BLISS-NEA, BLISS-SC, EMBRACE; n = 3638) after exclusion of patients with baseline NP BILAG A. Factors associated with NPSLE flare, defined as a new NP BILAG A or B, were investigated using Cox regression. In a subgroup analysis, we studied patients with baseline NP BILAG E for determinants of de novo NPSLE flare. Organ damage was assessed using the SLICC/ACR Damage Index (SDI).
Results: We documented 105 (2.9%) NPSLE flares. In multivariable analysis, male sex (HR = 2.37; 95% CI: 1.31, 4.28; P = 0.004), baseline NP BILAG B-D (HR = 5.91; 95% CI: 3.86, 9.06; P < 0.001), and increasing SDI scores (HR = 1.35; 95% CI: 1.21, 1.50; P < 0.001) were strongly associated with NPSLE flare. Belimumab use yielded no association at any dose or administration form. In analysis of SDI domains, NP damage was the strongest determinant of NPSLE flare (HR = 3.25; 95% CI: 2.72, 3.88; P < 0.001), holding true for cognitive impairment (HR = 14.29; 95% CI: 9.22, 22.14; P < 0.001), transverse myelitis (HR = 21.89; 95% CI: 5.40, 88.72; P < 0.001), and neuropathy (HR = 8.87; 95% CI: 5.59, 14.09; P < 0.001). Male sex was the strongest determinant of de novo NPSLE flare (HR = 3.26; 95% CI: 1.51, 7.04; P = 0.003).
Conclusion: Male sex, NPSLE history, and NP damage were strong determinants of impending NPSLE flare. No clear protection or predisposition was conferred from add-on belimumab.
Keywords: SLE; belimumab; determinants; flares; neuropsychiatric.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuropsychiatric involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus contributes to organ damage beyond the nervous system: a post-hoc analysis of 5 phase III randomized clinical trials.Rheumatol Int. 2024 Sep;44(9):1679-1689. doi: 10.1007/s00296-024-05667-5. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Rheumatol Int. 2024. PMID: 39115551 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of renal flares in systemic lupus erythematosus: a post-hoc analysis of four phase III clinical trials of belimumab.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2025 Feb 1;64(2):623-631. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae023. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2025. PMID: 38216728 Free PMC article.
-
Belimumab and antimalarials combined against renal flares in patients treated for extra-renal systemic lupus erythematosus: results from 4 phase III clinical trials.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 Feb 1;63(2):338-348. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kead253. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 37228028 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Organ damage in patients treated with belimumab versus standard of care: a propensity score-matched comparative analysis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Mar;78(3):372-379. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214043. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 30610066 Free PMC article.
-
Belimumab: review of use in systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Ther. 2012 May;34(5):1006-22. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.02.028. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Clin Ther. 2012. PMID: 22464040 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of anti-P ribosomal and anti-NR2 antibodies on depression and cognitive processes in SLE: an integrated clinical and functional MRI study.Lupus Sci Med. 2023 Nov;10(2):e001005. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2023-001005. Lupus Sci Med. 2023. PMID: 37918951 Free PMC article.
-
Sex- and gender-related differences in systemic lupus erythematosus: a scoping review.Rheumatol Int. 2025 Jun 27;45(7):160. doi: 10.1007/s00296-025-05910-7. Rheumatol Int. 2025. PMID: 40576834 Free PMC article.
-
The Challenge of Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: From Symptoms to Therapeutic Strategies.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 5;14(11):1186. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14111186. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893713 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dörner T, Furie R.. Novel paradigms in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 2019;393:2344–58. - PubMed
-
- Hanly JG. Diagnosis and management of neuropsychiatric SLE. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2014;10:338–47. - PubMed
-
- Bertsias GK, Boumpas DT.. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of neuropsychiatric SLE manifestations. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2010;6:358–67. - PubMed
-
- Hanly JG, Kozora E, Beyea SD, Birnbaum J.. Review: nervous system disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: current status and future directions. Arthritis Rheumatol 2019;71:33–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

