The effects of safinamide on dysphagia in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 37228084
- PMCID: PMC10212188
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286066
The effects of safinamide on dysphagia in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
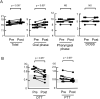
Dysphagia is a potentially fatal symptom of Parkinson's disease (PD) and is characterized by frequent silent aspiration, a risk factor for aspiration pneumonia. The transdermal dopamine agonist rotigotine alleviates dysphagia in patients with PD and is more effective than oral levodopa, suggesting the importance of continuous dopaminergic stimulation (CDS) in swallowing. Safinamide is a monoamine oxidase B (MAOB) inhibitor that facilitates CDS. In this retrospective open-label evaluator-blinded research, swallowing functions in nine patients with PD were examined using a video fluoroscopic swallowing study (VFSS) before and after treatment with 50 mg of oral safinamide. The VFSS results showed that safinamide significantly improved some swallowing measures during oral and pharyngeal phases, including oral transit time and pharyngeal transit time, without worsening of any measures. Notably, improvements in lip closure, an oral phase component, seemed to be most attributable to improvements in oral phase scores. In conclusion, a medicine for CDS may effectively improve swallowing functions in patients with PD. This is the first study to show that the MAOB inhibitor safinamide partly but significantly improves swallowing function in patients with PD.
Copyright: © 2023 Hirano et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest included: M. Hirano has received funding for speaker honoraria from Sumitomo, Ono, Otsuka, Novartis, Kyowa-Kirin, Eisai, and Takeda; and has received Grants-in-Aid from Japan’s Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology; AMED in Japan; and research support from Kindai University. M. Samukawa has received funding for speaker honoraria from Takeda, FP, Eisai, and Sumitomo Pharmaceutical. C. Isono reports no disclosures. Y. Nagai has received funding for speaker honoraria from Sumitomo, Kyowa-Kirin, Tanabe-Mitsubishi, Amgen, and Takeda; and has received Grants-in-Aid from Japan’s Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology; AMED in Japan. He also has received scholarship donation from Otsuka, Kyowa-Kirin, Tanabe-Mitsubishi, Fujimoto, Takeda, Sumitomo, Daiichi-Sankyo, Esai, and Chugai. These do not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

