Hsp90 mutants with distinct defects provide novel insights into cochaperone regulation of the folding cycle
- PMID: 37228112
- PMCID: PMC10246838
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010772
Hsp90 mutants with distinct defects provide novel insights into cochaperone regulation of the folding cycle
Abstract
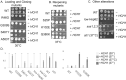
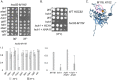
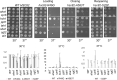
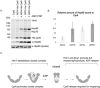
Molecular chaperones play a key role in maintaining proteostasis and cellular health. The abundant, essential, cytosolic Hsp90 (Heat shock protein, 90 kDa) facilitates the folding and activation of hundreds of newly synthesized or misfolded client proteins in an ATP-dependent folding pathway. In a simplified model, Hsp70 first helps load client onto Hsp90, ATP binding results in conformational changes in Hsp90 that result in the closed complex, and then less defined events result in nucleotide hydrolysis, client release and return to the open state. Cochaperones bind and assist Hsp90 during this process. We previously identified a series of yeast Hsp90 mutants that appear to disrupt either the 'loading', 'closing' or 'reopening' events, and showed that the mutants had differing effects on activity of some clients. Here we used those mutants to dissect Hsp90 and cochaperone interactions. Overexpression or deletion of HCH1 had dramatically opposing effects on the growth of cells expressing different mutants, with a phenotypic shift coinciding with formation of the closed conformation. Hch1 appears to destabilize Hsp90-nucleotide interaction, hindering formation of the closed conformation, whereas Cpr6 counters the effects of Hch1 by stabilizing the closed conformation. Hch1 and the homologous Aha1 share some functions, but the role of Hch1 in inhibiting progression through the early stages of the folding cycle is unique. Sensitivity to the Hsp90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922 also correlates with the conformational cycle, with mutants defective in the loading phase being most sensitive and those defective in the reopening phase being most resistant to the drug. Overall, our results indicate that the timing of transition into and out of the closed conformation is tightly regulated by cochaperones. Further analysis will help elucidate additional steps required for progression through the Hsp90 folding cycle and may lead to new strategies for modulating Hsp90 function.
Copyright: © 2023 Mercier et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Disrupting progression of the yeast Hsp90 folding pathway at different transition points results in client-specific maturation defects.Genetics. 2021 Mar 31;217(3):iyab009. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab009. Genetics. 2021. PMID: 33789348 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleotide-dependent interaction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Hsp90 with the cochaperone proteins Sti1, Cpr6, and Sba1.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jan;27(2):768-76. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01034-06. Epub 2006 Nov 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17101799 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the ATPase activity of hsp90 by the stress-regulated cochaperone aha1.Mol Cell. 2002 Dec;10(6):1307-18. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00785-2. Mol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12504007
-
The Hsp70-Hsp90 Chaperone Cascade in Protein Folding.Trends Cell Biol. 2019 Feb;29(2):164-177. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.10.004. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Trends Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 30502916 Review.
-
p23 and Aha1: Distinct Functions Promote Client Maturation.Subcell Biochem. 2023;101:159-187. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-14740-1_6. Subcell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36520307 Review.
Cited by
-
Ordered ATP hydrolysis in the Hsp90 chaperone is regulated by Aha1 and a conserved post-translational modification.Protein Sci. 2025 Jan;34(1):e5255. doi: 10.1002/pro.5255. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 39665290 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Hsp90 mechanism and in vivo functions learned from studies in the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Feb 8;11:1325590. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1325590. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38389899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of the conformational dynamics of the molecular chaperone Hsp90.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 4;15(1):8627. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52995-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39366960 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals unique Hsp90 cycle-dependent client interactions.Genetics. 2024 Jun 5;227(2):iyae057. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae057. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 38606935 Free PMC article.
-
Collaboration between two conserved sequence motifs drives ATPase stimulation of Hsp90 by Aha1.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 23:2025.06.10.658861. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.10.658861. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40667101 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

