Aesthetic Refinements in Male Chest Lifting
- PMID: 37228316
- PMCID: PMC10204266
- DOI: 10.1093/asjof/ojad021
Aesthetic Refinements in Male Chest Lifting
Abstract
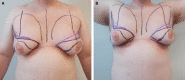
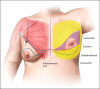
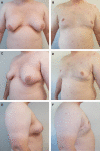
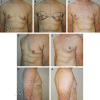
The authors describe aesthetic refinements to the approach for male chest lifting in male patients with grade 3 gynecomastia and/or significant chest skin excess. An inferior pedicle is used to transpose the nipple-areolar complex allowing preservation of pigment and sensation, liposuction and direct excision are used to reduce volume and excess skin, and the resulting curvilinear scar along the inferior and lateral border of the chest provide a more masculine appearance. Early experience with this technique has shown it to be safe and effective. Perioperative management and the detailed steps of the procedure are outlined.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Aesthetic Society.
Figures
References
-
- The Aesthetic Society's Cosmetic Surgery National Data Bank: Statistics 2021–2021. Aesthet Surg J. 2022;42(Supplement_1):1–18. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjac116 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
