Artificial Intelligence in Surgical Evaluation: A Study of Facial Rejuvenation Techniques
- PMID: 37228317
- PMCID: PMC10205049
- DOI: 10.1093/asjof/ojad032
Artificial Intelligence in Surgical Evaluation: A Study of Facial Rejuvenation Techniques
Abstract
Background: Aesthetic facial surgeries historically rely on subjective analysis in determining success; this limits objective comparison of surgical outcomes.
Objectives: This case study exemplifies the use of an artificial intelligence software on objectively analyzing facial rejuvenation techniques with the aim of reducing subjective bias.
Methods: Retrospectively, all patients who underwent facial rejuvenation surgery with concomitant procedures from 2015 to 2017 were included (n = 32). Patients were categorized into Groups A to C: Group A-10 superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) plication facelift (n = 10), Group B-SMASectomy facelift (n = 7), and Group C-high SMAS facelift (n = 15). Neutral repose images preoperatively and postoperatively (average >3 months) were analyzed using artificial intelligence for emotion and action unit alterations.
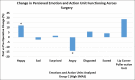
Results: Postoperatively, Group A experienced a decrease in happiness by 0.84% and a decrease in anger by 6.87% (P >> .1). Group B had an increase in happiness by 0.77% and an increase in anger by 1.91% (P >> .1). Both Group A and Group B did not show any discernable action unit patterns. In Group C, the lip corner puller AU increased in average intensity from 0% to 18.7%. This correlated with an average increase in detected happiness from 1.03% to 13.17% (P = .008). Conversely, the average detected anger decreased from 14.66% to 0.63% (P = .032).
Conclusions: This study provides the first proof of concept for the use of a machine learning software application to objectively assess various aesthetic surgical outcomes in facial rejuvenation. Due to limitations in patient heterogeneity, this study does not claim one technique's superiority but serves as a conceptual foundation for future investigation.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Aesthetic Society.
Figures



Comment in
-
Commentary on: Artificial Intelligence in Surgical Evaluation: A Study of Facial Rejuvenation Techniques.Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2023 Jun 14;5:ojad049. doi: 10.1093/asjof/ojad049. eCollection 2023. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2023. PMID: 37502410 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Using artificial intelligence to analyze emotion and facial action units following facial rejuvenation surgery.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2022 Sep;75(9):3628-3651. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2022.08.007. Epub 2022 Aug 5. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2022. PMID: 35989146
-
Lateral SMASectomy.Clin Plast Surg. 2019 Oct;46(4):523-532. doi: 10.1016/j.cps.2019.06.003. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Clin Plast Surg. 2019. PMID: 31514805 Review.
-
Facelift Surgery Turns Back the Clock: Artificial Intelligence and Patient Satisfaction Quantitate Value of Procedure Type and Specific Techniques.Aesthet Surg J. 2021 Aug 13;41(9):987-999. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjaa238. Aesthet Surg J. 2021. PMID: 33217756
-
Fat Grafting to Improve Results of Facelift: Systematic Review of Safety and Effectiveness of Current Treatment Paradigms.Aesthet Surg J. 2021 Jan 1;41(1):1-12. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjaa002. Aesthet Surg J. 2021. PMID: 31907534
-
Artificial intelligence for objectively measuring years regained after facial rejuvenation surgery.Am J Otolaryngol. 2023 Mar-Apr;44(2):103775. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103775. Epub 2022 Dec 26. Am J Otolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36706713
Cited by
-
Personalized Research on the Aging Face-A Narrative History.J Pers Med. 2024 Mar 26;14(4):343. doi: 10.3390/jpm14040343. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38672970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AI-Driven Assessment of Lip Volume Improvement Using Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: A Comprehensive Analysis.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 May 15. doi: 10.1007/s00266-025-04891-z. Online ahead of print. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 40374779
-
Impact of orthognathic surgery on emotional expression and smile aesthetics in Chinese patients as measured by FaceReader: a before-and-after study.Arch Craniofac Surg. 2025 Jun;26(3):115-123. doi: 10.7181/acfs.2025.0007. Epub 2025 Jun 20. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2025. PMID: 40624975 Free PMC article.
-
Commentary on: Artificial Intelligence in Surgical Evaluation: A Study of Facial Rejuvenation Techniques.Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2023 Jun 14;5:ojad049. doi: 10.1093/asjof/ojad049. eCollection 2023. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2023. PMID: 37502410 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Using Artificial Intelligence to Quantify Sexual Dimorphism in Aesthetic Faces: Analysis of 100 Facial Points in 42 Caucasian Celebrities.Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2023 Jun 5;5:ojad046. doi: 10.1093/asjof/ojad046. eCollection 2023. Aesthet Surg J Open Forum. 2023. PMID: 37441561 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ekman P, Friesen W. Facial Action Coding System: A Technique for the Measurement of Facial Movement. Consulting Psychologists Press; 1978.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
