Purtscher's Retinopathy After Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation: A Literature Review
- PMID: 37228527
- PMCID: PMC10206335
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.38033
Purtscher's Retinopathy After Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation: A Literature Review
Abstract
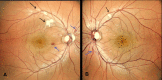
Purtscher's retinopathy is a rare angiopathy reported in patients with a history of severe trauma and other systemic diseases. The diagnosis is made on clinical grounds, and the severity varies. A 41-year-old gentleman with underlying poorly controlled diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia was referred to the ophthalmology department for diabetic retinopathy screening. He denied visual complaints. Ocular examination revealed a negative relative afferent pupillary defect with a visual acuity of 6/6 bilaterally. The anterior segment examination was unremarkable. Both eye (oculus uterque, OU) fundus revealed a pink disc with a cup-to-disc ratio of 0.4 and peripapillary flame-shaped hemorrhages. Right eye (oculus dexter, OD) also showed multiple cotton wool spots along the superotemporal arcade involving zones 1 and 2 of the retina, while left eye (oculus sinister, OS) showed a single cotton wool spot along the superotemporal arcade at zone 1 of the retina. Otherwise, there were no visible retinal emboli, dot hemorrhages, or hard exudates, and the macula was normal. The retinal features were not characteristic of diabetic retinopathy. It mimicked hypertensive retinopathy, but the patient was normotensive. The absence of inner retinal thickening and hyperreflectivity on optical coherence tomography of the macula ruled out retinal vein occlusion. This prompted us to elicit further history, and the patient disclosed a recent admission for myocardial infarction in which he received cardiopulmonary resuscitation with chest compressions for seven minutes. Hence, the diagnosis of OU Purtscher's retinopathy was made, and the patient was monitored closely in the clinic. Purtscher's retinopathy remains a diagnostic dilemma and should not be neglected in complex clinical contexts.
Keywords: cardiac resuscitation; chest compression; cotton wool spot; purtscher's retinopathy; retinal hemorrhages; traumatic retinal angiopathy.
Copyright © 2023, Balasubaramaniam et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A case of bilateral endogenous endophthalmitis misdiagnosed as Purtscher's retinopathy.BMC Ophthalmol. 2020 Apr 6;20(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12886-020-01399-9. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32252687 Free PMC article.
-
Purtscher's Retinopathy Following Long Bone Fracture: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Jan 28;16(1):e53087. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53087. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38414683 Free PMC article.
-
Purtscher's retinopathy associated with acute pancreatitis.Optom Vis Sci. 2014 Feb;91(2):e43-51. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000000132. Optom Vis Sci. 2014. PMID: 24362324
-
Purtscher's retinopathy.Optometry. 2002 Mar;73(3):166-72. Optometry. 2002. PMID: 12365700 Review.
-
Purtscher's and Purtscher-like retinopathy etiology, features, management, and outcomes: A summative systematic review of 168 cases.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 6;19(9):e0306473. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306473. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39240905 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical features of retinopathy after cardiopulmonary resuscitation.BMC Ophthalmol. 2023 Sep 21;23(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s12886-023-03137-3. BMC Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37735637 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tripathy K, Patel BC. StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; Purtscher retinopathy. - PubMed
-
- Purtscher's and Purtscher-like retinopathies: a review. Agrawal A, McKibbin MA. Surv Ophthalmol. 2006;51:129–136. - PubMed
-
- Pseudo-rétinopathie de Purtscher: à propos d’un cas et revue de la littérature. Pina JP, Ssi-Yan-Kai K, de Monchy I, et al. J Fr D'ophtalmol. 2008;31:609–613. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
