Marijuana as a Cause of Diffuse Coronary Vasospasm Leading to Cardiac Arrest
- PMID: 37228539
- PMCID: PMC10205149
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.38026
Marijuana as a Cause of Diffuse Coronary Vasospasm Leading to Cardiac Arrest
Abstract
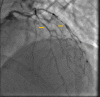
Marijuana is considered as the most popular illicit drug around the world. It has numerous cardiovascular effects with myocardial infarction (MI) being a lethal one. The negative physiological effects of marijuana are well-studied, including tachycardia, nausea, memory impairment, anxiety, panic, and arrhythmia. We present a case of cardiac arrest following marijuana use in a patient who had a normal electrocardiogram (EKG) on presentation but diffuse coronary vasospasm on left heart catheterization (LHC) with no obstructive lesion. The patient had a transient episode of ST elevation on EKG following the procedure which resolved with an increased dose of nitroglycerine drip. Synthetic cannabinoids are more potent and not detected on a regular urine drug screen (UDS). In patients with low risk for cardiovascular events, particularly young adults, presenting with symptoms of MI/cardiac arrest, marijuana-induced MI should be suspected due to the severe adverse effects of its synthetic component.
Keywords: cardiac arrest; coronary spasm; illicit drugs; marijuana use; st myocardial infarction.
Copyright © 2023, Khan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Coronary Vasospasm Associated With Synthetic Marijuana Resulting in Transient Electrocardiogram Changes and Troponin Elevation.Cureus. 2022 May 17;14(5):e25084. doi: 10.7759/cureus.25084. eCollection 2022 May. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35719796 Free PMC article.
-
Marijuana-induced Coronary Vasospasm with Persistent Inter-coronary Connection: A Case Report and Review of Literature.Cureus. 2019 Jun 1;11(6):e4799. doi: 10.7759/cureus.4799. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31497413 Free PMC article.
-
Vasopressor-Induced Generalized Coronary Vasospasm Presenting as Inferior ST-Segment Elevation in Post-Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation.JACC Case Rep. 2019 Aug 21;1(2):94-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2019.05.023. eCollection 2019 Aug. JACC Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 34316757 Free PMC article.
-
Catheter-induced Vasospasm of the Anatomically Normal Right Coronary Artery in a Patient With Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction and Obstructive Disease in the Left Anterior Descending Artery; A Challenging Case Report and Review of the Literature.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023 Jan;48(1):101432. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2022.101432. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36170909 Review.
-
Multiple coronary vasospasm: a cause of repeated myocardial infarction and symptomatic 'torsade de pointes' (atypical ventricular tachycardia). A case presentation and review.S Afr Med J. 1983 Jan 22;63(4):103-12. S Afr Med J. 1983. PMID: 6336853 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthetic Cannabinoid (Mojo)-Induced ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: A Case Report.Cureus. 2025 May 21;17(5):e84570. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84570. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40546626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acute intoxication caused by synthetic cannabinoids 5F-ADB and MMB-2201: a case series. Barceló B, Pichini S, López-Corominas V, Gomila I, Yates C, Busardò FP, Pellegrini M. Forensic Sci Int. 2017;273:0–4. - PubMed
-
- The "new" marijuana. Wells DL, Ott CA. Ann Pharmacother. 2011;45:414–417. - PubMed
-
- Marijuana as a trigger of cardiovascular events: speculation or scientific certainty? Aryana A, Williams MA. Int J Cardiol. 2007;118:141–144. - PubMed
-
- Electrocardiographic effects of marihuana. Kochar MS, Hosko MJ. JAMA. 1973;225:25–27. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
