Preclinical models and evaluation criteria of prostatitis
- PMID: 37228599
- PMCID: PMC10203503
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1183895
Preclinical models and evaluation criteria of prostatitis
Abstract
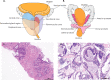
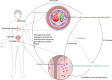
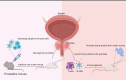
Prostatitis is a common urological condition that affects almost half of all men at some point in their life. The prostate gland has a dense nerve supply that contributes to the production of fluid to nourish sperm and the mechanism to switch between urination and ejaculation. Prostatitis can cause frequent urination, pelvic pain, and even infertility. Long-term prostatitis increases the risk of prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia. Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis presents a complex pathogenesis, which has challenged medical research. Experimental studies of prostatitis require appropriate preclinical models. This review aimed to summarize and compare preclinical models of prostatitis based on their methods, success rate, evaluation, and range of application. The objective of this study is to provide a comprehensive understanding of prostatitis and advance basic research.
Keywords: animal models; chronic non-bacterial prostatitis; evaluation criteria; infectious prostatitis; prostatitis.
Copyright © 2023 He, Luo, Xu, Qian, Zou, Zhang, Zeng and Zou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

