Inhibition of NO Production in LPS-Stimulated Primary Rat Glial Cells by Gnidilatimonoein and Extract of Daphne mucronata
- PMID: 37228631
- PMCID: PMC10203186
- DOI: 10.30498/ijb.2023.285965.3052
Inhibition of NO Production in LPS-Stimulated Primary Rat Glial Cells by Gnidilatimonoein and Extract of Daphne mucronata
Abstract
Background: In the CNS, glial cells are involved in neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain. The glial cells are activated by a variety of pathological conditions and release pro-inflammatory mediators, including nitric oxide (NO). Overexpression of iNOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase) and extra NO is detrimental to neurophysiology and neuronal viability.
Objectives: This study aimed to examine the effect of Gnidilatimonein isolated from D. mucronata and its leaves extract (as natural phytochemicals) on NO production in the LPS-induced primary glial cells.
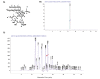
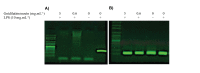
Materials and methods: A preparative HPLC method was used to isolate gnidilatimonoein from leaves ethanolic extract. Various doses of Gnidilatimonoein, the ethanolic extract were applied to primary glial cells inflamed by lipopolysaccharide. A Colorimetric test, an MTT assay, and a RT-PCR analysis were then performed to analyze and compare NO production, cell viability, and iNOS expression.
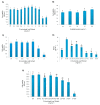
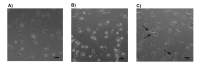
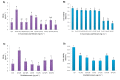
Results: Gnidilatimonoein treatment of pretreated primary glial cells significantly inhibited iNOS expression and decreased NO synthesis. Plant extracts also reduced NO production in inflamed microglial and glial at 0.1-3 mg.mL-1. At these concentrations, none of these compounds exerted a cytotoxic effect, suggesting that their anti-inflammatory effects were not due to the death of cells.
Conclusion: This study indicates that D. mucronata and its active compound, Gnidilatimonoein, could have restrained effects on the expression of iNOS on the induced glial cells; however, further investigation is warranted.
Keywords: Anti-neuroinflammation; Glial; Gnidilatimonoein; Nitric Oxide; Daphne mucronata.
Copyright: © 2021 The Author(s); Published by Iranian Journal of Biotechnology.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
