Alternative Complement Pathway Inhibition by Lampalizumab: Analysis of Data From Chroma and Spectri Phase III Clinical Trials
- PMID: 37228694
- PMCID: PMC10205501
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xops.2023.100286
Alternative Complement Pathway Inhibition by Lampalizumab: Analysis of Data From Chroma and Spectri Phase III Clinical Trials
Abstract
Purpose: Lampalizumab, an antigen-binding fragment of a humanized monoclonal antibody directed against complement factor D (CFD), is designed to treat geographic atrophy (GA) secondary to age-related macular degeneration. Given the lack of clinical efficacy observed in patients with GA in the phase III Chroma/Spectri trials, we investigated the impact of lampalizumab on the complement system in vivo. We developed 6 novel assays to measure changes in complement pathway activities in aqueous humor samples collected from patients enrolled in these trials.
Design: Chroma/Spectri were double-masked, sham-controlled, 96-week trials.
Participants: Aqueous humor samples from 97 patients with bilateral GA across all groups (i.e., intravitreous lampalizumab 10 mg every 6 weeks, every 4 weeks, or corresponding sham procedures) were tested.
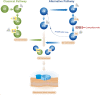
Methods: Novel antibody capture assays were developed on the Simoa platform for complement factor B (CFB), the Bb fragment of CFB, intact complement component 3 (C3), processed C3, intact complement component 4 (C4), and processed C4.
Main outcome measures: The ratio of processed vs. intact complement factors (i.e., complement activity) in aqueous humor were assessed.
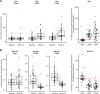
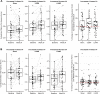
Results: Patients treated with either of the lampalizumab regimens demonstrated an increase in CFD level at week 24 compared with baseline, along with a corresponding median reduction in the Bb:CFB ratio of 41% to 43%. There were no strong correlations between lampalizumab concentrations in aqueous humor and change in CFD levels or Bb:CFB ratio over time. No change in downstream C3 processing was observed with lampalizumab treatment. Additionally, there was no change in C4 processing.
Conclusions: The collection of aqueous humor samples from patients in Chroma and Spectri trials provided key insights on the effects of lampalizumab, a novel complement inhibitor, on local ocular complement activation. Lampalizumab inhibited the alternative complement pathway in the eyes of patients with GA; however, this did not translate into a measurable reduction in either classical or total complement activity, based on absence of changes in C4 and C3 processing, respectively.
Financial disclosures: Proprietary or commercial disclosure may be found after the references.
Keywords: Alternative complement pathway; Antibody conjugate assay; Chroma and Spectri trials; Geographic atrophy; Lampalizumab.
© 2023 by the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
Figures

References
-
- Flaxman S.R., Bourne R.R.A., Resnikoff S., et al. Global causes of blindness and distance vision impairment 1990–2020: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2017;5:e1221–e1234. - PubMed
-
- Holz F.G., Strauss E.C., Schmitz-Valckenberg S., van Lookeren Campagne M. Geographic atrophy: clinical features and potential therapeutic approaches. Ophthalmology. 2014;121:1079–1091. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

