Metagenomic next-generation sequencing confirms the diagnosis of Legionella pneumonia with rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney injury in a limited resource area: a case report and review
- PMID: 37228720
- PMCID: PMC10205016
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1145733
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing confirms the diagnosis of Legionella pneumonia with rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney injury in a limited resource area: a case report and review
Abstract
Background: Legionella pneumonia, rhabdomyolysis, and acute kidney injury are called the Legionella triad, which is rare and associated with a poor outcome and even death. Early diagnosis and timely treatment are essential for these patients.
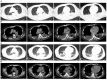
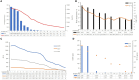
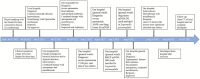
Case presentation: A 63-year-old man with cough, fever, and fatigue was initially misdiagnosed with common bacterial infection and given beta-lactam monotherapy but failed to respond to it. Conventional methods, including the first Legionella antibody test, sputum smear, and culture of sputum, blood, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were negative. He was ultimately diagnosed with a severe infection of Legionella pneumophila by metagenomics next-generation sequencing (mNGS). This patient, who had multisystem involvement and manifested with the rare triad of Legionella pneumonia, rhabdomyolysis, and acute kidney injury, finally improved after combined treatment with moxifloxacin, continuous renal replacement therapy, and liver protection therapy.
Conclusion: Our results showed the necessity of early diagnosis of pathogens in severe patients, especially in Legionnaires' disease, who manifested with the triad of Legionella pneumonia, rhabdomyolysis, and acute kidney injury. mNGS may be a useful tool for Legionnaires' disease in limited resource areas where urine antigen tests are not available.
Keywords: Legionella pneumonia; acute kidney injury; case report; metagenomic next-generation sequencing; rhabdomyolysis.
Copyright © 2023 Du, Feng, Wang, Huang, Tao and Mao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Legionella pneumonia complicated with severe acute kidney injury requiring continuous renal replacement therapy: a case series.J Med Case Rep. 2025 Jul 13;19(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s13256-025-05407-8. J Med Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40653483 Free PMC article.
-
Legionella pneumonia complicated by rhabdomyolysis.BMJ Case Rep. 2019 Jun 20;12(6):e229243. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2019-229243. BMJ Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31227570 Free PMC article.
-
[Legionnaires' disease complicated by rhabdomyolysis and acute renal failure: about a case].Pan Afr Med J. 2016 Jun 9;24:126. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2016.24.126.8536. eCollection 2016. Pan Afr Med J. 2016. PMID: 27642464 Free PMC article. French.
-
Pathological evidence of rhabdomyolysis-induced acute tubulointerstitial nephritis accompanying Legionella pneumophila pneumonia.J Clin Pathol. 2008 Sep;61(9):1062-3. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2008.057000. Epub 2008 Jun 13. J Clin Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18552170 Review.
-
[Legionnaires' disease with pronounced cerebellar involvement: case report and literature review].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2020 Feb 12;43(2):126-131. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-0939.2020.02.010. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32062882 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Community-Acquired Pneumonia with Acute Kidney Injury Complicated by Rhabdomyolysis- A Challenging Case Report in Resource Limit Setting.Int Med Case Rep J. 2024 Nov 1;17:895-901. doi: 10.2147/IMCRJ.S492874. eCollection 2024. Int Med Case Rep J. 2024. PMID: 39502308 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple pulmonary cavities in an immunocompetent patient: a case report and literature review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 27;11:1329381. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1329381. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38476447 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid metagenomics next-generation sequencing on the diagnosis and management of patients with suspected pulmonary infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 23;15:1521641. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1521641. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40625833 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

