Cost-effectiveness analysis of COVID-19 screening strategy under China's dynamic zero-case policy
- PMID: 37228729
- PMCID: PMC10203195
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1099116
Cost-effectiveness analysis of COVID-19 screening strategy under China's dynamic zero-case policy
Abstract
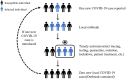
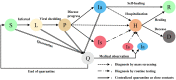
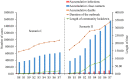
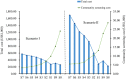
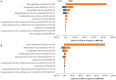
This study aims to optimize the COVID-19 screening strategies under China's dynamic zero-case policy through cost-effectiveness analysis. A total of 9 screening strategies with different screening frequencies and combinations of detection methods were designed. A stochastic agent-based model was used to simulate the progress of the COVID-19 outbreak in scenario I (close contacts were promptly quarantined) and scenario II (close contacts were not promptly quarantined). The primary outcomes included the number of infections, number of close contacts, number of deaths, the duration of the epidemic, and duration of movement restriction. Net monetary benefit (NMB) and the incremental cost-benefit ratio were used to compare the cost-effectiveness of different screening strategies. The results indicated that under China's COVID-19 dynamic zero-case policy, high-frequency screening can help contain the spread of the epidemic, reduce the size and burden of the epidemic, and is cost-effective. Mass antigen testing is not cost-effective compared with mass nucleic acid testing in the same screening frequency. It would be more cost-effective to use AT as a supplemental screening tool when NAT capacity is insufficient or when outbreaks are spreading very rapidly.
Keywords: COVID-19; China; agent-based model; cost-effectiveness; dynamic zero-case policy; screening strategy.
Copyright © 2023 Li and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Joint Prevention Control Mechanism of the State Council . COVID-19 Disease Prevention and Control Guideline. (2022). Available online at: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-06/28/content_5698168.htm (accessed September 18, 2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

