PD-L1: expression regulation
- PMID: 37228770
- PMCID: PMC10205351
- DOI: 10.1097/BS9.0000000000000149
PD-L1: expression regulation
Abstract
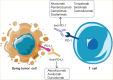
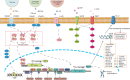
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), expressed on the surface of tumor cells, can bind to programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) on T cells. The interaction of PD-1 and PD-L1 can inhibit T-cell responses by decreasing T-cell activity and accelerating their apoptosis. Various cancers express high levels of PD-L1 and exploit PD-L1/PD-1 signaling to evade T-cell immunity, and immunotherapies targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis have been shown to exert remarkable anti-tumor effects; however, not all tumor patients benefit from these therapies. Therefore, study of the mechanisms regulating PD-L1 expression are imperative. In this review, we explore regulation of PD-L1 expression in the contexts of gene transcription, signaling pathways, histone modification and remodeling, microRNAs, long noncoding RNAs, and post-translational modification. Current developments in studies of agents that block PD-L1 and correlations between immunotherapies targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and PD-L1 expression are also summarized. Our review will assist in understanding of PD-L1 expression regulation and discusses the implications of reported findings in cancer diagnosis and immunotherapy.
Keywords: Drug discovery; Epigenetics; Immune checkpoint blockage; Immunotherapy; PD-L1 expression.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health Inc., on behalf of the Chinese Medical Association (CMA) and Institute of Hematology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College (IHCAMS).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms Controlling PD-L1 Expression in Cancer.Mol Cell. 2019 Nov 7;76(3):359-370. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.09.030. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Mol Cell. 2019. PMID: 31668929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PD-1/PD-L1 axis regulation in cancer therapy: The role of long non-coding RNAs and microRNAs.Life Sci. 2020 Sep 1;256:117899. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117899. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32504749 Review.
-
Functional Expression of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (B7-H1) by Immune Cells and Tumor Cells.Front Immunol. 2017 Aug 10;8:961. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00961. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28848559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic strategies synergize with PD-L1/PD-1 targeted cancer immunotherapies to enhance antitumor responses.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 May;10(5):723-733. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.09.006. Epub 2019 Sep 25. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 32528824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Regulation of PD-L1 posttranslational modification and its application progress in tumor immunotherapy].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Nov;38(11):1036-1043. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36328434 Chinese.
Cited by
-
PGM5-AS1 Promotes Progression of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Immune Escape by Regulating miR-503-5p.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul 1;17:4187-4197. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S453245. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38973995 Free PMC article.
-
Polymeric Micellar Paclitaxel Plus Cisplatin Combined With Tislelizumab as the First-Line Treatment of Advanced Unresectable Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Phase II Study.Thorac Cancer. 2025 Apr;16(7):e70055. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.70055. Thorac Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40228531 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
PD-L1 Expression in NSCLC: Clouds in a Bright Sky.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 24;26(13):6066. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136066. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pembrolizumab-induced simultaneous and multiple immune-related adverse events including myasthenia gravis, myositis, hepatitis, and pityriasis lichenoides in a non-small cell lung cancer patient.Arch Clin Cases. 2025 Feb 6;12(1):17-21. doi: 10.22551/2025.46.1201.10306. eCollection 2025. Arch Clin Cases. 2025. PMID: 39925987 Free PMC article.
-
High percentage of bone marrow CD8+ tissue-resident-like memory T cells predicts inferior survival in patients with acute myeloid leukemia.Blood Sci. 2024 Jun 7;6(3):e00194. doi: 10.1097/BS9.0000000000000194. eCollection 2024 Jul. Blood Sci. 2024. PMID: 38854481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K, Chen L. B7-H1, a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med. 1999;5(12):1365–1369. - PubMed
-
- Schmid P, Rugo HS, Adams S, et al. ; IMpassion130 Investigators. Atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel as first-line treatment for unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (IMpassion130): updated efficacy results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(1):44–59. - PubMed
-
- Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. ; IMbrave150 Investigators. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(20):1894–1905. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials