Hydatid Disease of Tibia Reconstructed with Allograft: A Rare Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 37228885
- PMCID: PMC10204905
- DOI: 10.4103/jwas.jwas_286_22
Hydatid Disease of Tibia Reconstructed with Allograft: A Rare Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
Background: Hydatid disease of bone shows a well-defined, multiloculated lytic lesion with the appearance of a bunch of grapes. The presenting symptoms are pain and swelling with or without pathological fracture. The treatment options include surgery followed by a long duration of albendazole. Removal of the involved bone is required to decrease the chances of recurrences.
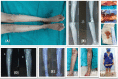
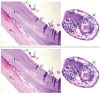
Case report: In our study, we have included a case of 28-year-old woman presented with complaints of pain and difficulty in weight bearing over her right lower limb for 2.5 months. Radiograph suggested an eccentric lytic lesion in midshaft of tibia and biopsy revealed granulosus cyst wall, nucleate germinal layer, the brood capsule, and protoscolices with visible hooklets. Patient was subjected to surgery with the excision of cyst along with extended curettage of bone creating a bone defect around the lesion and with anterolateral platting with coverage of bone defect by allogenic bone grafting. Patient was kept on above knee slab with non-weight-bearing mobilization for 6 weeks. Postoperative chemotherapy with Albendazole was given for 3 months. Patient was followed up every 6 weeks for 3 months and every month thereafter on outpatient basis. Return to work and patient satisfaction were excellent.
Conclusion: Definitive Surgical management with Preoperative and postoperative chemotherapy seems to be effective to avoid recurrence. The bone defect caused by the disease or surgery can be managed with a bone graft either of autograft or allograft.
Keywords: Allogenic bone graft; echinococcosis; hydatid cyst; skeletal hydatosis; tibia.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of the West African College of Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hydatid cyst of the tibia.J Postgrad Med. 1992 Oct-Dec;38(4):194-5, 197. J Postgrad Med. 1992. PMID: 1307592
-
Composite treatment for primary long-bone hydatidosis.Orthopedics. 2012 Dec;35(12):e1826-31. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20121120-34. Orthopedics. 2012. PMID: 23218646 Review.
-
Osteogenic protein-1 for long bone nonunion: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005;5(6):1-57. Epub 2005 Apr 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2005. PMID: 23074475 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Hydatid Cyst in a Child Managed with Albendazole.J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2023 Mar 10;20(3):804-807. doi: 10.33314/jnhrc.v20i3.4385. J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2023. PMID: 36974879
-
Hydatidosis of infratemporal fossa with proptosis - an unusual presentation: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2018 Oct 17;12(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s13256-018-1812-y. J Med Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 30326941 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Primary seronegative intermuscular hydatidosis in a child, an infection that should be approached like a tumor: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2024 Mar 8;18(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s13256-024-04405-6. J Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38454461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathological Fracture of the Tibia Due to Lytic Bone Lesion Caused by Hydatidosis with Absence of Systemic Involvement: A Case Report and Review of Literature.Acta Parasitol. 2025 May 9;70(3):102. doi: 10.1007/s11686-025-01041-y. Acta Parasitol. 2025. PMID: 40343559 Review.
References
-
- Torricelli P, Martinelli C, Biagini R, Ruggieri P, De Cristofaro R. Radiographic and computed tomographic findings in hydatid disease of bone. Skeletal Radiol. 1990;19:435–9. - PubMed
-
- Kalinova K, Proichev V, Stefanova P, Tokmakova K, Poriazova E. Hydatid bone disease: A case report and review of the literature. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2005;13:323–5. - PubMed
-
- Zlitni M, Ezzaouia K, Lebib H, Karray M, Kooli M, Mestiri M. Hydatid cyst of bone: Diagnosis and treatment. World J Surg. 2001;25:75–82. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
