Rare diagnosis of coexistent antiphospholipid syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus in a male patient with successful management: a case report
- PMID: 37228943
- PMCID: PMC10205281
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000556
Rare diagnosis of coexistent antiphospholipid syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus in a male patient with successful management: a case report
Abstract
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are two autoimmune disorders that can develop together or separately. Similarities in the pathogenesis have been discovered, including the production of autoantibodies that target subcellular antigens and shared elevated risk of cardiovascular morbidity, which may be caused by common pathologic pathways.
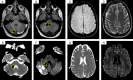
Case presentation: A 28-year-old male, referred to our hospital for the assessment of chest pain. Past medical history was significant for extensive deep venous thrombosis despite the appropriate management with a therapeutic dose of direct-acting oral anticoagulant. Prolonged partial thromboplastin time was not corrected by mixing study along with positive lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin, and B-2 glycoprotein antibodies. In addition, antinuclear antibodies, anti-DNA antibodies, and direct Coombs were positive with decreased levels of C3. The patient was diagnosed with SLE with brain, heart, and kidney involvement in the setting of antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. He was treated successfully with full recovery.
Discussion: SLE and APS both have sneaky ways of manifestation. Ineffective diagnosis and therapy could cause irreversible organ damage. Clinicians should have a high index of suspicion for APS, particularly in young patients who approach with spontaneous or unprovoked thromboses or unexplained recurrent early or late pregnancy loss. Anticoagulation, modifying cardiovascular risk factors, and identifying and treating any underlying inflammatory diseases are all part of the multidisciplinary care that is needed for management.
Conclusion: Although male affection is rare, SLE and APS should be considered in male patients as these conditions tend to be more aggressive than in the female.
Keywords: antiphospholipid syndrome; autoimmune; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial conflict of interest with regard to the content of this report.
Figures
References
-
- Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, et al. . International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J Thromb Haemost 2006;4:295–306. - PubMed
-
- Cervera R, Piette JC, Font J, et al. . Antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical and immunologic manifestations and patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1000 patients. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46:1019–1027. - PubMed
-
- Chambers SA, Allen E, Rahman A, et al. . Damage and mortality in a group of British patients with systemic lupus erythematosus followed up for over 10 years. Rheumatology 2009;48:673–675. - PubMed
-
- Erkan D, Yazici Y, Sobel R, et al. . Primary antiphospholipid syndrome: functional outcome after 10 years. J Rheumatol 2000;27:2817–2821. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous