A successful process of treatment with necrotizing fasciitis of upper extremities in patients with diabetes mellitus: a case report
- PMID: 37228965
- PMCID: PMC10205320
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000000463
A successful process of treatment with necrotizing fasciitis of upper extremities in patients with diabetes mellitus: a case report
Abstract
Necrotizing fasciitis (NF) represents a rapidly progressive, life-threatening infection involving the fascia and subcutaneous tissue. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to treat, especially in diabetic patients.
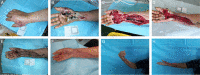
Case presentation: This case report presents on a patient with diabetes mellitus rapidly developed a NF of the upper extremities following a minor trauma in the palmar of greater thenar. In the initial stages of her hospital admission, severe hand soft tissue infection, and systemic toxicity is the most prominent clinical manifestation. During her hospitalization, efficacious multidisciplinary treatment was carried out to avoid severe consequences.
Clinical discussion and conclusion: The objective of this case report is to present a successful individual strategy in a complex case to standardize the treatment process. Accurate and standardized management can improve the prognosis of patients affected from upper extremities NF of diabetic avoiding and severe complications and saving lives.
Keywords: case report; diabetes mellitus; necrotizing fasciitis.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Baiu I, Staudenmayer K. Necrotizing soft tissue infections. JAMA 2019;321:1738. - PubMed
-
- Wilson B. Necrotizing fasciitis. Am Surg 1952;18:416–431. - PubMed
-
- Centers C. for Disease, Prevention, Tropical diabetic hand syndrome–Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, 1998-2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2002;51:969–970. - PubMed
-
- Leiblein M, Marzi I, Sander AL, et al. . Necrotizing fasciitis: treatment concepts and clinical results. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2018;44:279–290. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
