Recent Developments in Nanotechnology-Based Biosensors for the Diagnosis of Coronavirus
- PMID: 37229148
- PMCID: PMC10040920
- DOI: 10.1007/s11468-023-01822-z
Recent Developments in Nanotechnology-Based Biosensors for the Diagnosis of Coronavirus
Abstract
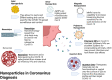
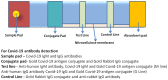
The major challenge in today's world is that medical research is facing the existence of a vast number of viruses and their mutations, which from time to time cause outbreaks. Also, the continuous and spontaneous mutations occurring in the viruses and the emergence of resistant virus strains have become serious medical hazards. So, in view of the growing number of diseases, like the recent COVID-19 pandemic that has caused the deaths of millions of people, there is a need to improve rapid and sensitive diagnostic strategies to initiate timely treatment for such conditions. In the cases like COVID-19, where a real cure due to erratic and ambiguous signs is not available, early intervention can be life-saving. In the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries, nanotechnology has evolved exponentially and can overcome multiple obstacles in the treatment and diagnosis of diseases. Nanotechnology has developed exponentially in the biomedical and pharmaceutical fields and can overcome numerous challenges in the treatment and diagnosis of diseases. At the nano stage, the molecular properties of materials such as gold, silver, carbon, silica, and polymers get altered and can be used for the creation of reliable and accurate diagnostic techniques. This review provides insight into numerous diagnostic approaches focused on nanoparticles that could have been established for quick and early detection of such diseases.
Keywords: COVID-19; Diagnostic approach; SARS-CoV; Viral diagnostics.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing InterestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Countries where COVID-19 has spread [cited 2022 December 20]. Available from: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/countries-where-coronavirus-ha...
-
- Nanotechnology in battle against coronavirus [cited 2022 December 20]. Available from: https://statnano.com/nanotechnology-in-battle-against-coronavirus
-
- Nanotechnology vs. Viruses [cited 2022 December 20]. Available from: https://www.nanowerk.com/spotlight/spotid=60291.php
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
