Photoresponsive hydrogel-based soft robot: A review
- PMID: 37229213
- PMCID: PMC10205512
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100657
Photoresponsive hydrogel-based soft robot: A review
Abstract
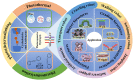
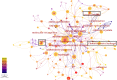
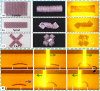
Soft robots have received a lot of attention because of their great human-robot interaction and environmental adaptability. Most soft robots are currently limited in their applications due to wired drives. Photoresponsive soft robotics is one of the most effective ways to promote wireless soft drives. Among the many soft robotics materials, photoresponsive hydrogels have received a lot of attention due to their good biocompatibility, ductility, and excellent photoresponse properties. This paper visualizes and analyzes the research hotspots in the field of hydrogels using the literature analysis tool Citespace, demonstrating that photoresponsive hydrogel technology is currently a key research direction. Therefore, this paper summarizes the current state of research on photoresponsive hydrogels in terms of photochemical and photothermal response mechanisms. The progress of the application of photoresponsive hydrogels in soft robots is highlighted based on bilayer, gradient, orientation, and patterned structures. Finally, the main factors influencing its application at this stage are discussed, including the development directions and insights. Advancement in photoresponsive hydrogel technology is crucial for its application in the field of soft robotics. The advantages and disadvantages of different preparation methods and structures should be considered in different application scenarios to select the best design scheme.
Keywords: Actuators; Citespace; Photoresponsive hydrogels; Response mechanisms; Soft robots; Structural forms.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Programmable Morphing Hydrogels for Soft Actuators and Robots: From Structure Designs to Active Functions.Acc Chem Res. 2022 Jun 7;55(11):1533-1545. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.2c00046. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Acc Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 35413187
-
Self-Healing Approach toward Catalytic Soft Robots.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022 Sep 14;14(36):40590-40598. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c09889. Epub 2022 Aug 29. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022. PMID: 36039512
-
Polydopamine-Modified MXene-Integrated Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) to Construct Ultrafast Photoresponsive Bilayer Hydrogel Actuators with Smart Adhesion.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023 Oct 25;15(42):49689-49700. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c12203. Epub 2023 Oct 12. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023. PMID: 37823839
-
Controllable Preparation and Research Progress of Photosensitive Antibacterial Complex Hydrogels.Gels. 2023 Jul 13;9(7):571. doi: 10.3390/gels9070571. Gels. 2023. PMID: 37504450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muscle-like hydrogels with fast isochoric responses and their applications as soft robots: a minireview.Mater Horiz. 2025 Feb 3;12(3):719-733. doi: 10.1039/d4mh01187b. Mater Horiz. 2025. PMID: 39530734 Review.
Cited by
-
Conducting polymer hydrogels based on supramolecular strategies for wearable sensors.Exploration (Beijing). 2024 Mar 14;4(5):20220167. doi: 10.1002/EXP.20220167. eCollection 2024 Oct. Exploration (Beijing). 2024. PMID: 39439497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A highly stretchable, self-adhesive, antimicrobial conductive hydrogel with guar gum/acrylic acid/MXene@AgNPs for multifunctional wearable sensors and electromagnetic interference shielding.RSC Adv. 2025 Mar 27;15(12):9430-9442. doi: 10.1039/d5ra00159e. eCollection 2025 Mar 21. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40151532 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogel-Based Continuum Soft Robots.Gels. 2025 Mar 27;11(4):254. doi: 10.3390/gels11040254. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40277689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep Cleaning of Crystal Violet and Methylene Blue Dyes from Aqueous Solution by Dextran-Based Cryogel Adsorbents.Gels. 2024 Aug 23;10(9):546. doi: 10.3390/gels10090546. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39330148 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogel-Based Biointerfaces: Recent Advances, Challenges, and Future Directions in Human-Machine Integration.Gels. 2025 Mar 23;11(4):232. doi: 10.3390/gels11040232. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40277668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu Y., Du H., Liu L., Leng J. Shape memory polymers and their composites in aerospace applications: a review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014;23 doi: 10.1088/0964-1726/23/2/023001. - DOI
-
- Du X., Cui H., Xu T., Huang C., Wang Y., Zhao Q., Xu Y., Wu X. Reconfiguration, camouflage, and color-shifting for bioinspired adaptive hydrogel-based millirobots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020;30 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201909202. - DOI
-
- Xiao Y.Y., Jiang Z.C., Zhao Y. Liquid crystal poly merased soft robots. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020 doi: 10.1002/aisy.202000148. - DOI
-
- Lee C., Kim M., Kim Y.J., Hong N., Ryu S., Kim H.J., Kim S. Soft robot review. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2017;15:3–15. doi: 10.1007/s12555-016-0462-3. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

