Synthesis, structure, and properties of switchable cross-conjugated 1,4-diaryl-1,3-butadiynes based on 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene
- PMID: 37229218
- PMCID: PMC10204205
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.19.49
Synthesis, structure, and properties of switchable cross-conjugated 1,4-diaryl-1,3-butadiynes based on 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene
Abstract
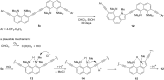
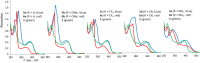
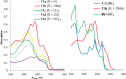
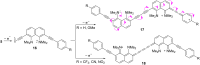
A set of novel 1,4-diaryl-1,3-butadiynes terminated by two 7-(arylethynyl)-1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene fragments was prepared via the Glaser-Hay oxidative dimerization of 2-ethynyl-7-(arylethynyl)-1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalenes. The oligomers synthesized in this way are cross-conjugated systems, in which two conjugation pathways are possible: π-conjugation of 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene (DMAN) fragments through a butadiyne linker and a donor-acceptor aryl-C≡C-DMAN conjugation path. The conjugation path can be "switched" simply by protonation of DMAN fragments. X-ray diffraction, UV-vis spectroscopy and cyclic voltammetry are applied to analyze the extent of π-conjugation and the efficiency of particular donor-acceptor conjugation path in these new compounds. X-ray structures and absorption spectra of doubly protonated tetrafluoroborate salts of the oligomers are also discussed.
Keywords: 1,4-diaryl-1,3-butadiynes; 1,8-bis(dimethylamino)naphthalene; Glaser–Hay reaction; cross-conjugated systems; donor–acceptor systems.
Copyright © 2023, Tsybulin et al.
Figures


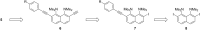
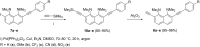






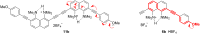

References
-
- Forrest S R, Thompson M E, editors. Organic, Electronics, Optoelectronics. Chem Rev. 2007;107:923–1386.
-
- Miller R D, Chandross E A, editors. Materials for Electronics. Chem Rev. 2010;110:1–574. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
