Impact of thyroid hormone perturbations in adult mice: brain weight and blood vessel changes, gene expression variation, and neurobehavioral outcomes
- PMID: 37229849
- PMCID: PMC10247485
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2023.04.012
Impact of thyroid hormone perturbations in adult mice: brain weight and blood vessel changes, gene expression variation, and neurobehavioral outcomes
Abstract
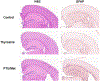
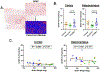
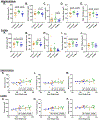
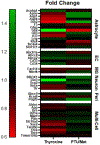
Mouse models of hyper- and hypothyroidism were used to examine the effects of thyroid hormone (TH) dyshomeostasis on the aging mammalian brain. 13-14 month-old mice were treated for 4months with either levothyroxine (hyperthyroid) or a propylthiouracil and methimazole combination (PTU/Met; hypothyroid). Hyperthyroid mice performed better on Morris Water Maze than control mice, while hypothyroid mice performed worse. Brain weight was increased in thyroxine-treated, and decreased in PTU/Met-treated animals. The brain weight change was strongly correlated with circulating and tissue T4. Quantitative measurements of microvessels were compared using digital neuropathologic methods. There was an increase in microvessel area in hyperthyroid mice. Hypothyroid mice showed a trend for elevated glial fibrillary acidic protein-immunoreactive astrocytes, indicating an increase in neuroinflammation. Gene expression alterations were associated with TH perturbation and astrocyte-expressed transcripts were particularly affected. For example, expression of Gli2 and Gli3, mediators in the Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway, were strongly impacted by both treatments. We conclude that TH perturbations produce robust neurobehavioral, pathological, and brain gene expression changes in aging mouse models.
Keywords: Astrocytes; Collagen IV; Digital neuropathology; Hyperthyroidism; Hypothyroidism; ScanScope.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure statement The authors have no actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Age effect on thyroid hormone brain response in male mice.Endocrine. 2019 Dec;66(3):596-606. doi: 10.1007/s12020-019-02078-6. Epub 2019 Sep 7. Endocrine. 2019. PMID: 31494803
-
Effects of experimentally induced maternal hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism on the development of rat offspring: I. The development of the thyroid hormones-neurotransmitters and adenosinergic system interactions.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2010 Oct;28(6):437-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2010.06.007. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20599606
-
Fasting-induced increase in type II iodothyronine deiodinase activity and messenger ribonucleic acid levels is not reversed by thyroxine in the rat hypothalamus.Endocrinology. 1998 Jun;139(6):2879-84. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.6.6062. Endocrinology. 1998. PMID: 9607797
-
Thyroid hormone regulates the expression of the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway in the embryonic and adult Mammalian brain.Endocrinology. 2011 May;152(5):1989-2000. doi: 10.1210/en.2010-1396. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Endocrinology. 2011. PMID: 21363934 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Related Resistance to Thyroid Hormone Action.Drugs Aging. 2019 Nov;36(11):1007-1014. doi: 10.1007/s40266-019-00711-7. Drugs Aging. 2019. PMID: 31512083 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurovascular unit disruption and blood-brain barrier leakage in MCT8 deficiency.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2023 Nov 3;20(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12987-023-00481-w. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2023. PMID: 37924081 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid dysfunction and Alzheimer's disease, a vicious circle.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 14;15:1354372. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1354372. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38419953 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barez-Lopez S, Grijota-Martinez C, Auso E, Fernandez-de Frutos M, Montero-Pedrazuela A, Guadano-Ferraz A 2019. Adult Mice Lacking Mct8 and Dio2 Proteins Present Alterations in Peripheral Thyroid Hormone Levels and Severe Brain and Motor Skill Impairments. Thyroid 29(11), 1669–82. doi: 10.1089/thy.2019.0068. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blevins BL, Vinters HV, Love S, Wilcock DM, Grinberg LT, Schneider JA, Kalaria RN, Katsumata Y, Gold BT, Wang DJJ, Ma SJ, Shade LMP, Fardo DW, Hartz AMS, Jicha GA, Nelson KB, Magaki SD, Schmitt FA, Teylan MA, Ighodaro ET, Phe P, Abner EL, Cykowski MD, Van Eldik LJ, Nelson PT 2021. Brain arteriolosclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 141(1), 1–24. doi: 10.1007/s00401-020-02235-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

