GEANT4-DNA simulation of temperature-dependent and pH-dependent yields of chemical radiolytic species
- PMID: 37230081
- PMCID: PMC11556437
- DOI: 10.1088/1361-6560/acd90d
GEANT4-DNA simulation of temperature-dependent and pH-dependent yields of chemical radiolytic species
Abstract
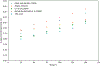
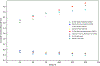
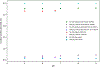
Objective.GEANT4-DNA can simulate radiation chemical yield (G-value) for radiolytic species such as the hydrated electron (eaq-) with the independent reaction times (IRT) method, however, only at room temperature and neutral pH. This work aims to modify the GEANT4-DNA source code to enable the calculation ofG-values for radiolytic species at different temperatures and pH values.Approach.In the GEANT4-DNA source code, values of chemical parameters such as reaction rate constant, diffusion coefficient, Onsager radius, and water density were replaced by corresponding temperature-dependent polynomials. The initial concentration of hydrogen ion (H+)/hydronium ion (H3O+) was scaled for a desired pH using the relationship pH = -log10[H+]. To validate our modifications, two sets of simulations were performed. (A) A water cube with 1.0 km sides and a pH of 7 was irradiated with an isotropic electron source of 1 MeV. The end time was 1μs. The temperatures varied from 25 °C to 150 °C. (B) The same setup as (A) was used, however, the temperature was set to 25 °C while the pH varied from 5 to 9. The results were compared with published experimental and simulated work.Main results.The IRT method in GEANT4-DNA was successfully modified to simulateG-values for radiolytic species at different temperatures and pH values. Our temperature-dependent results agreed with experimental data within 0.64%-9.79%, and with simulated data within 3.52%-12.47%. The pH-dependent results agreed well with experimental data within 0.52% to 3.19% except at a pH of 5 (15.99%) and with simulated data within 4.40%-5.53%. The uncertainties were below ±0.20%. Overall our results agreed better with experimental than simulation data.Significance.Modifications in the GEANT4-DNA code enabled the calculation ofG-values for radiolytic species at different temperatures and pH values.
Keywords: GEANT4-DNA; radiation chemical yield; radiation chemistry; water radiolysis.
Creative Commons Attribution license.
Figures



References
-
- Allen AO 1961. The radiation chemistry of water and aqueous solutions (New York: D. Van Nostrand Company; )
-
- Autsavapromporn N, Meesungnoen J, Plante I and Jay-Gerin J-P 2007. Monte Carlo simulation study of the effects of acidity and let on the primary free-radical and molecular yields of water radiolysis application to the Fricke dosimeter Can. J. Chem 85 214–29
-
- Bartels DM, Henshaw J and Sims HE 2013. Modeling the critical hydrogen concentration in the aecl test reactor Radiat. Phys. Chem 82 16–24
-
- Berg HC 1993. Random Walks in Biology (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press; )
