Impact of digital economic development and environmental pollution on residents' health: an empirical analysis based on 279 prefecture-level cities in China
- PMID: 37231366
- PMCID: PMC10212741
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-023-15788-4
Impact of digital economic development and environmental pollution on residents' health: an empirical analysis based on 279 prefecture-level cities in China
Abstract
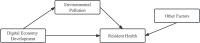
Background: The digital economy based on the internet and IT is developing rapidly in China, which makes a profound impact on urban environmental quality and residents' health activities. Thus, this study introduces environmental pollution as a mediating variable based on Grossman's health production function to explore the impact of digital economic development on the health of the population and its influence path.
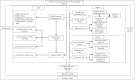
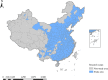
Methods: Based on the panel data of 279 prefecture-level cities in China from 2011 to 2017, this paper investigates the acting mechanism of digital economic development on residents' health by employing a combination of mediating effects model and spatial Durbin model.
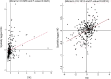
Results: The development of digital economy makes direct improvement on residents' health condition, which is also obtained indirectly by means of environmental pollution mitigation. Besides, from the perspective of spatial spillover effect, the development of digital economy also has a significant promoting effect on the health of adjacent urban residents, and further analysis reveals that the promoting effect in the central and western regions of China is more pronounced than that in the eastern region.
Conclusions: Digital economy can have a direct promoting effect on the health of residents, and environmental pollution has an intermediary effect between digital economy and residents' health; At the same time, there is also a regional heterogeneity among the three relationships. Therefore, this paper believes that the government should continue to formulate and implement scientific digital economy development policies at the macro and micro levels to narrow the regional digital divide, improve environmental quality and enhance the health level of residents.
Keywords: Digital economic development; Environmental pollution; Mediating effect; Residents’ health; Spatial Durbin model.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Re-evaluating the impact and mechanism of digital economy on regional pollution intensity from the perspective of spatial spillover.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Feb;31(6):9062-9077. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-31794-w. Epub 2024 Jan 6. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38182959
-
The impact of digital economy on environmental pollution: Evidence from 267 cities in China.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 26;19(1):e0297009. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297009. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38277347 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between Digital Economy and Environmental Pollution: New Evidence from a Spatial Perspective.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 21;19(9):5074. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095074. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35564469 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Digital Economy on Residents' Health: Based on the Perspective of Population Ageing.Front Public Health. 2021 Jul 26;9:725971. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.725971. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34381758 Free PMC article.
-
Path to pollution and carbon reduction synergy from the perspective of the digital economy: Fresh evidence from 292 prefecture-level cities in China.Environ Res. 2024 Jul 1;252(Pt 4):119050. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.119050. Epub 2024 May 8. Environ Res. 2024. PMID: 38729414 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of digital finance on elderly physical health: Evidence from China.Digit Health. 2025 Jun 25;11:20552076251353318. doi: 10.1177/20552076251353318. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40574885 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental pollution, trade openness and the health of middle-aged and elderly people: an analysis of threshold effect based on data from 111 prefecture-level cities in China.Arch Public Health. 2024 Nov 5;82(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s13690-024-01429-8. Arch Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39501307 Free PMC article.
-
Can the digital economy foster advancements in the healthcare sector? - a case study using interprovincial data from China.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jan 17;25(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21372-9. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39825273 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of environmental regulation, energy technology innovation on population health.BMC Public Health. 2025 May 2;25(1):1635. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22877-z. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40316950 Free PMC article.
-
Does digital economy development enhance Chinese residents' health? Impact and mechanism.BMC Public Health. 2025 Mar 26;25(1):1154. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22325-y. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40140993 Free PMC article.
References
-
- OECD, Digital Economy. Outlook 2015. [10.1787/9789264232440-en] Accessed 1 June 2022.
-
- Schwab K. The fourth industrial revolution. Currency; 2017.p.6–13.
-
- Ye X, Hong SH, Song WS, Kim YC, Zhang X. An industry 4.0 Asset Administration Shell-Enabled Digital Solution for Robot-Based Manufacturing Systems. Ieee Access. 2021;9:154448–59. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3128580. - DOI
-
- Boyes H, Hallaq B, Cunningham J, Watson T. The industrial internet of things (IIoT): an analysis framework. Comput Ind. 2018;101:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2018.04.015. - DOI
-
- Central People’s Government of. the People’ s Republic of China.Made in China 2025. [http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2015-05/19/content_2864538.htm]. Accessed 5 Oct 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

