The prolactin receptor scaffolds Janus kinase 2 via co-structure formation with phosphoinositide-4,5-bisphosphate
- PMID: 37232489
- PMCID: PMC10260020
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.84645
The prolactin receptor scaffolds Janus kinase 2 via co-structure formation with phosphoinositide-4,5-bisphosphate
Abstract
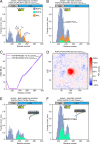
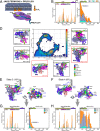
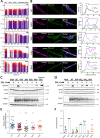
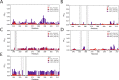
Class 1 cytokine receptors transmit signals through the membrane by a single transmembrane helix to an intrinsically disordered cytoplasmic domain that lacks kinase activity. While specific binding to phosphoinositides has been reported for the prolactin receptor (PRLR), the role of lipids in PRLR signaling is unclear. Using an integrative approach combining nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, cellular signaling experiments, computational modeling, and simulation, we demonstrate co-structure formation of the disordered intracellular domain of the human PRLR, the membrane constituent phosphoinositide-4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2) and the FERM-SH2 domain of the Janus kinase 2 (JAK2). We find that the complex leads to accumulation of PI(4,5)P2 at the transmembrane helix interface and that the mutation of residues identified to interact specifically with PI(4,5)P2 negatively affects PRLR-mediated activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 (STAT5). Facilitated by co-structure formation, the membrane-proximal disordered region arranges into an extended structure. We suggest that the co-structure formed between PRLR, JAK2, and PI(4,5)P2 locks the juxtamembrane disordered domain of the PRLR in an extended structure, enabling signal relay from the extracellular to the intracellular domain upon ligand binding. We find that the co-structure exists in different states which we speculate could be relevant for turning signaling on and off. Similar co-structures may be relevant for other non-receptor tyrosine kinases and their receptors.
Keywords: IDP; JAK2; NMR; human; integrative structural biology; molecular biophysics; simulation; single pass receptor; structural biology.
© 2023, Araya-Secchi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
RA, KB, PS, AP, GH, KL, SP, LA, BK No competing interests declared
Figures
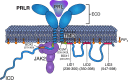
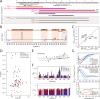
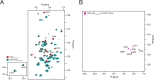

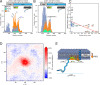





Update of
References
-
- Abraham MJ, Murtola T, Schulz R, Páll S, Smith JC, Hess B, Lindahl E. GROMACS: high performance molecular Simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX. 2015;1–2:19–25. doi: 10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001. - DOI
-
- Aksamitiene E, Achanta S, Kolch W, Kholodenko BN, Hoek JB, Kiyatkin A. Prolactin-stimulated activation of Erk1 / 2 mitogen-activated protein Kinases is controlled by Pi3-kinase / RAC / PAK signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. Cellular Signalling. 2011;23:1794–1805. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.06.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

