Preventing, Mitigating, and Treating Women's Perinatal Mental Health Problems during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Scoping Review of Reviews with a Qualitative Narrative Synthesis
- PMID: 37232595
- PMCID: PMC10215147
- DOI: 10.3390/bs13050358
Preventing, Mitigating, and Treating Women's Perinatal Mental Health Problems during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Scoping Review of Reviews with a Qualitative Narrative Synthesis
Abstract
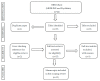
Meeting the mental health needs of perinatal women during the COVID-19 pandemic is a serious concern. This scoping review looks at how to prevent, mitigate or treat the mental health problems faced by women during a pandemic, and lays out suggestions for further research. Interventions for women with pre-existing mental health problems or health problems that develop during the perinatal period are included. The literature in English published in 2020-2021 is explored. Hand searches were conducted in PubMed and PsychINFO using the terms COVID-19, perinatal mental health and review. A total of 13 systematic and scoping reviews and meta-analyses were included. This scoping review shows that every woman should be assessed for mental health issues at every stage of her pregnancy and postpartum, with particular attention to women with a history of mental health problems. In the COVID-19 era, efforts should be focused on reducing the magnitude of stress and a perceived sense of lack of control experienced by perinatal women. Helpful instructions for women with perinatal mental health problems include mindfulness, distress tolerance skills, relaxation exercises, and interpersonal relationship building skills. Further longitudinal multicenter cohort studies could help improve the current knowledge. Promoting perinatal resilience and fostering positive coping skills, mitigating perinatal mental health problems, screening all prenatal and postpartum women for affective disorders, and using telehealth services appear to be indispensable resources. In future, governments and research agencies will need to pay greater attention to the trade-offs of reducing the spread of the virus through lockdowns, physical distancing, and quarantine measures and developing policies to mitigate the mental health impact on perinatal women.
Keywords: COVID-19; mitigation; perinatal mental health; prevention; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conceptual framework on barriers and facilitators to implementing perinatal mental health care and treatment for women: the MATRIx evidence synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2024 Jan;12(2):1-187. doi: 10.3310/KQFE0107. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2024. PMID: 38317290
-
Perinatal mental health and women's lived experience of the COVID-19 pandemic: A scoping review of the qualitative literature 2020-2021.Midwifery. 2023 Aug;123:103706. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2023.103706. Epub 2023 May 1. Midwifery. 2023. PMID: 37167674 Free PMC article.
-
A cross-national study of factors associated with women's perinatal mental health and wellbeing during the COVID-19 pandemic.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 21;16(4):e0249780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249780. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33882096 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal and perinatal health: a scoping review.Reprod Health. 2021 Jan 18;18(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12978-021-01070-6. Reprod Health. 2021. PMID: 33461593 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources