Application of Silk-Fibroin-Based Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering
- PMID: 37233022
- PMCID: PMC10218181
- DOI: 10.3390/gels9050431
Application of Silk-Fibroin-Based Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering
Abstract
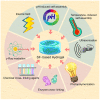
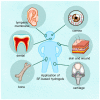
Silk fibroin (SF) is an excellent protein-based biomaterial produced by the degumming and purification of silk from cocoons of the Bombyx mori through alkali or enzymatic treatments. SF exhibits excellent biological properties, such as mechanical properties, biocompatibility, biodegradability, bioabsorbability, low immunogenicity, and tunability, making it a versatile material widely applied in biological fields, particularly in tissue engineering. In tissue engineering, SF is often fabricated into hydrogel form, with the advantages of added materials. SF hydrogels have mostly been studied for their use in tissue regeneration by enhancing cell activity at the tissue defect site or counteracting tissue-damage-related factors. This review focuses on SF hydrogels, firstly summarizing the fabrication and properties of SF and SF hydrogels and then detailing the regenerative effects of SF hydrogels as scaffolds in cartilage, bone, skin, cornea, teeth, and eardrum in recent years.
Keywords: bone; cartilage; cornea; hydrogel; scaffolds; silk fibroin; skin; tissue engineering; tooth; tympanic membrane; wounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Silk Hydrogel for Tissue Engineering: A Review.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2022 Apr 1;23(4):467-477. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2022. PMID: 35945843 Review.
-
Preparation of silk fibroin/hyaluronic acid hydrogels with enhanced mechanical performance by a combination of physical and enzymatic crosslinking.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2021 Aug;32(12):1635-1653. doi: 10.1080/09205063.2021.1932070. Epub 2021 Jun 24. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2021. PMID: 34004124
-
The Contribution of Silk Fibroin in Biomedical Engineering.Insects. 2022 Mar 14;13(3):286. doi: 10.3390/insects13030286. Insects. 2022. PMID: 35323584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Injectable Ultrasonication-Induced Silk Fibroin Hydrogel for Cartilage Repair and Regeneration.Tissue Eng Part A. 2021 Sep;27(17-18):1213-1224. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2020.0323. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021. PMID: 33353462
-
Silk fibroin for skin injury repair: Where do things stand?Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020 Jan 1;153:28-53. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2019.09.003. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020. PMID: 31678360 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrospun Silk-ICG Composite Fibers and the Application toward Hemorrhage Control.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Sep 19;15(9):272. doi: 10.3390/jfb15090272. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39330247 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue engineering approaches for dental pulp regeneration: The development of novel bioactive materials using pharmacological epigenetic inhibitors.Bioact Mater. 2024 Jun 12;40:182-211. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.06.012. eCollection 2024 Oct. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38966600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in Hydrogels: A Comprehensive Review of Natural and Synthetic Innovations for Biomedical Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jul 24;17(15):2026. doi: 10.3390/polym17152026. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40808075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Could an Anterior Cruciate Ligament Be Tissue-Engineered from Silk?Cells. 2023 Sep 25;12(19):2350. doi: 10.3390/cells12192350. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37830564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfibre-Functionalised Silk Hydrogels.Cells. 2023 Dec 20;13(1):10. doi: 10.3390/cells13010010. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38201214 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parween S., Bhatnagar I., Bhosale S., Paradkar S., Michael I.J., Rao C.M., Asthana A. Cross-linked chitosan biofunctionalized paper-based microfluidic device towards long term stabilization of blood typing antibodies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020;163:1233–1239. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.075. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ealla K., Veeraraghavan V.P., Ravula N.R., Durga C.S., Ramani P., Sahu V., Poola P.K., Patil S., Panta P. Silk Hydrogel for Tissue Engineering: A Review. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2022;23:467–477. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

