The Positive Impact of Early Frailty Levels on Mortality in Elderly Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis Undergoing Transcatheter/Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement
- PMID: 37233180
- PMCID: PMC10218811
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd10050212
The Positive Impact of Early Frailty Levels on Mortality in Elderly Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis Undergoing Transcatheter/Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement
Abstract
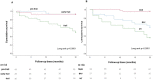
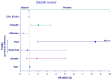
Background: Frailty is highly common in older patients (pts) undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), and it is associated with poor outcomes. The selection of patients who can benefit from this procedure is necessary and challenging. The aim of the present study is to evaluate outcomes in older severe aortic valve stenosis (AS) pts, selected by a multidisciplinary approach for surgical, clinical, and geriatric risk and referred to treatment, according to frailty levels. Methods: A total of 109 pts (83 ± 5 years; females, 68%) with AS were classified by Fried's score in pre-frail, early frail, and frail and underwent surgical aortic valve replacement SAVR/TAVR, balloon aortic valvuloplasty, or medical therapy. We evaluated geriatric, clinical, and surgical features and detected periprocedural complications. The outcome was all-cause mortality. Results: Increasing frailty was associated with the worst clinical, surgical, geriatric conditions. By using Kaplan-Meier analysis, the survival rate was higher in pre-frail and TAVR groups (p < 0.001) (median follow-up = 20 months). By using the Cox regression model, frailty (p = 0.004), heart failure (p = 0.007), EF% (p = 0.043), albumin (p = 0.018) were associated with all-cause mortality. Conclusions: According to tailored frailty management, elderly AS pts with early frailty levels seem to be the most suitable candidates for TAVR/SAVR for positive outcomes because advanced frailty would make each treatment futile or palliative.
Keywords: aortic stenosis; frailty; mortality; pre-frailty; transcatheter aortic valve replacement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Otto C.M., Nishimura R.A., Bonow R.O., Carabello B.A., Erwin J.P., 3rd, Gentile F., Jneid H., Krieger E.V., Mack M., Mcleod C., et al. 2020 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2021;143:e35–e71. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000932. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Leon M.B., Smith C.R., Mack M., Miller D.C., Moses J.W., Svensson L.G., Tuzcu E.M., Webb J.G., Fontana G.P., Makkar R.R., et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve implantation for aortic stenosis in patients who cannot undergo surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010;363:1597–1607. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1008232. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Reynolds M.R., Magnuson E.A., Wang K., Thourani V.H., Williams M., Zajarias A., Rihal C.S., Brown D.L., Smith C.R., Leon M.B., et al. Health-related quality of life after transcatheter or surgical aortic valve replacement in high-risk patients with severe aortic stenosis: Results from the PARTNER (Placement of AoRTic TraNscathetER Valve) Trial (Cohort A) J. Am. Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:548–558. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.03.075. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

