Diagnostic accuracy of circulating exosomal circRNAs in malignances: A meta-analysis and systematic review
- PMID: 37233410
- PMCID: PMC10219741
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033872
Diagnostic accuracy of circulating exosomal circRNAs in malignances: A meta-analysis and systematic review
Abstract
Background: Pathogenesis of malignant tumors are often accompanied by aberrant expression of circular RNAs (circRNAs), indicating the potential diagnostic value of circRNAs in tumors. CircRNAs have been found to be enriched, stable and ubiquitous in serum and plasma exosomes. The study aims at evaluating the diagnostic performance of circulating (plasma and serum) exosomal circRNA in different types of cancer by synthesis of published data.
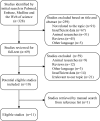
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, Medline and the Web of Science databases to identify potentially eligible studies published before April 2021. We conducted the meta-analysis following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses recommendations.
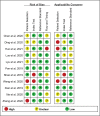
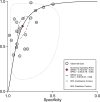
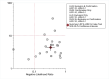
Results: Eleven articles comprising 21 studies were included, and a total of 1609 cases and 1498 controls were evaluated. Six types of cancer were involved in these studies, including lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, colorectal cancer, gastric cancer, multiple myeloma and osteosarcoma. The pooled sensitivity and specificity were 0.72 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.62-0.81) and 0.83 (95% CI, 0.78-0.88), respectively. Summary receiver operating characteristic curve was constructed and the pooled value of area under curve was 0.86 (95% CI, 0.83-0.89), indicating a favorable diagnostic efficacy of circulating exosomal circRNAs in malignancies.
Conclusions: In conclusion, our study evaluated the diagnostic power of circulating exosomal circRNAs in 6 types of cancer by synthesis of published data comprising 21 studies from eleven articles. The pooled analysis provided the evidence supporting circulating exosomal circRNAs as a promising noninvasive diagnostic biomarkers for malignancies.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Novel potential tumor biomarkers: Circular RNAs and exosomal circular RNAs in gastrointestinal malignancies.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jul;34(7):e23359. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23359. Epub 2020 May 17. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32419229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormally Expressed Circular RNAs are Promising Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: a Meta-Analysis.Clin Lab. 2019 Nov 1;65(11). doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2019.190354. Clin Lab. 2019. PMID: 31710441
-
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Utility of Circular RNAs as Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 May 2;2019:1684039. doi: 10.1155/2019/1684039. eCollection 2019. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31187026 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance of circular RNAs in human cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Jul;7(7):e00749. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.749. Epub 2019 May 20. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 31106993 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of circular RNAs in colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pathol Res Pract. 2019 Dec;215(12):152680. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152680. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Pathol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 31635986
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNA as a potential diagnostic biomarker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2023 Sep 21;18(9):e0291921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291921. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37733767 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of exosomal noncoding RNA in lung cancer: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Apr 17;14:1357248. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1357248. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38694786 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic accuracy of urine-derived exosomes for bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2024 Oct 29;22(1):285. doi: 10.1186/s12957-024-03569-1. World J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39472962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. . Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–49. - PubMed
-
- Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, et al. . Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:363–85. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. . Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

