Identification of the active ingredients and pharmacological effects of Kuntai capsules in the treatment of primary ovarian insufficiency: A review
- PMID: 37233423
- PMCID: PMC10219746
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033884
Identification of the active ingredients and pharmacological effects of Kuntai capsules in the treatment of primary ovarian insufficiency: A review
Abstract
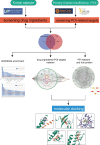
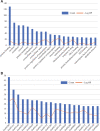
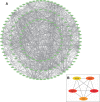
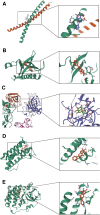
Kuntai capsules are effective in controlling primary ovarian insufficiency (POI). However, the precise mechanisms underlying the pharmacological effects of Kuntai capsules remain unclear. This study aimed to screen the active components and underlying mechanisms of Kuntai capsules for POI treatment using network pharmacology protocols and molecular docking technology. Potential active constituents in the chemical composition of Kuntai capsules were obtained from the Traditional Chinese Medicine System Pharmacology Database. Targets for POI were obtained from the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man and Gene Cards database. All target data were integrated to identify the active ingredients of POI treatment. Enrichment analyses were performed using the Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery database. The STRING database and Cytoscape software were used for protein-protein interaction network construction and core target identification. Finally, a molecular docking analysis of the active components and core targets was performed. A total of 157 ingredients related to POI were identified. Enrichment analysis showed that these components might participate in the mitogen-activated protein kinase, tumor necrosis factor, phosphoinositide-3-kinase/AKT serine/threonine kinase 1, and forkhead box O signaling pathways. Further protein-protein interaction network analysis revealed that the core targets were Jun proto-oncogene, AKT serine/threonine kinase 1, tumor protein P53, interleukin 6, and the epidermal growth factor receptor. Molecular docking analysis showed that baicalein was the most active ingredient with the highest affinity for the core targets. This study identified baicalein as the core functional component and elucidated the potential pharmacological effects of Kuntai capsule in the treatment of POI.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potential therapeutic drug targets and pathways prediction for premature ovarian insufficiency -Based on network pharmacologic method.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Mar 25;304:116054. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.116054. Epub 2022 Dec 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36526095
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on the mechanism of Wensan tincture in the treatment of pulmonary nodules: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Nov 29;103(48):e40648. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040648. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39612458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network pharmacology and experimental validation to explore the molecular mechanisms of Bushen Huoxue for the treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):10345-10362. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1996317. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34753385 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking-based analyses to predict the potential mechanism of Huangqin decoction in treating colorectal cancer.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Jul 6;11(19):4553-4566. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i19.4553. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37469733 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of peach kernel and safflower herb-pair for the treatment of liver fibrosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Apr 21;102(16):e33593. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033593. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37083803 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Additional effects of herbal medicine combined with bisphosphonates for primary osteoporosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 13;15:1413515. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1413515. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39346562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giri R, Vincent AJ. Prevalence and risk factors of premature ovarian insufficiency/early menopause. Semin Reprod Med. 2020;38:237–46. - PubMed
-
- Stuenkel CA, Gompel A. Primary ovarian insufficiency. N Engl J Med. 2023;388:154–63. - PubMed
-
- McGlacken-Byrne SM, Conway GS. Premature ovarian insufficiency. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2022;81:98–110. - PubMed
-
- Golezar S, Ramezani Tehrani F, Khazaei S, et al. . The global prevalence of primary ovarian insufficiency and early menopause: a meta-analysis. Climacteric. 2019;22:403–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

