A Bibliometric and In Silico-Based Analysis of Anti-Lung Cancer Compounds from Sea Cucumber
- PMID: 37233477
- PMCID: PMC10223633
- DOI: 10.3390/md21050283
A Bibliometric and In Silico-Based Analysis of Anti-Lung Cancer Compounds from Sea Cucumber
Abstract
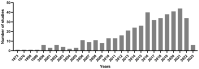
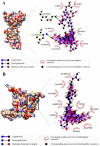
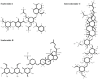
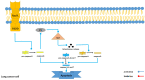
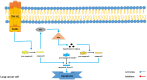
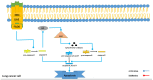
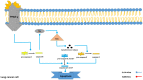
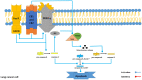
Lung cancer is one of the most lethal malignancies in the world. However, current curative approaches for treating this type of cancer have some weaknesses. Therefore, scientists are attempting to discover new anti-lung cancer agents. Sea cucumber is a marine-derived source for discovering biologically active compounds with anti-lung cancer properties. To explore the anti-lung cancer properties of sea cucumber, we analyzed surveys using VOSviewer software and identified the most frequently used keywords. We then searched the Google Scholar database for compounds with anti-lung cancer properties within that keyword family. Finally, we used AutoDock 4 to identify the compounds with the highest affinity for apoptotic receptors in lung cancer cells. The results showed that triterpene glucosides were the most frequently identified compounds in studies examining the anti-cancer properties of sea cucumbers. Intercedenside C, Scabraside A, and Scabraside B were the three triterpene glycosides with the highest affinity for apoptotic receptors in lung cancer cells. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that anti-lung cancer properties of sea cucumber-derived compounds have been examined in in silico conditions. Ultimately, these three components displayed anti-lung cancer properties in in silico conditions and may be used for the manufacture of anti-lung cancer agents in the near future.
Keywords: anti-cancer agents; apoptosis; bibliometrics; glucosides; in silico techniques; lung neoplasms; marine biology; sea cucumbers; triterpenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors Afshin Zare, Amin Tamadon, and Nader Tanideh were employed by PerciaVista R&D Co. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Wargasetia T.L., Permana S. The role of sea cucumber active compound and its derivative as an anti-cancer agent. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018;4:27–32. doi: 10.1007/s40495-018-0121-x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

